In the ever-evolving digital world, Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have emerged as a revolutionary concept, reshaping the way we perceive value and ownership online. But what exactly are NFTs, and why are they so important? Let’s delve into the fascinating world of NFTs.
Table of Contents
What are NFTs?

Non-Fungible Tokens, or NFTs, have become a buzzword in the digital world, but what exactly are they? Let’s break it down.
NFT Meaning
At their core, NFTs are a type of digital asset. They exist on a blockchain, which is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger that records transactions across many computers. The term “non-fungible” means that these tokens are unique and cannot be replaced with something else. This is in contrast to “fungible” tokens, like Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are identical to each other and can be exchanged on a one-to-one basis.
Explanation of the term “non-fungible”
To understand NFTs, it’s important to understand the concept of fungibility. If something is fungible, it means it can be exchanged for another identical item. For example, one dollar bill is fungible with another dollar bill. They are identical and hold the same value. Non-fungible, then, means that each item is unique and cannot be replaced with something else. A plane ticket, for example, is non-fungible as it has specific information (passenger name, destination, date and time, etc.) that makes it different from other tickets.
How NFTs Differ from Other Types of Digital Assets
NFTs stand apart from other digital assets due to their uniqueness. Each NFT has a digital signature that distinguishes it from other tokens. This means that each NFT can represent something unique and can prove ownership of that unique item or piece of content.
For example, digital art can be tokenized as an NFT, and the owner of the NFT is the official owner of that piece of art. The information about the artwork and its owner is stored on the blockchain, providing a transparent and tamper-proof record of ownership.
NFTs represent a new way of owning and trading unique assets in the digital world. They have opened up new possibilities for digital artists, collectors, gamers, and many others, and are set to play a significant role in the future of the digital economy.
The History of NFTs

The history of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) is relatively short, but it’s packed with significant milestones that have shaped the digital landscape. Let’s take a journey through the evolution of NFTs.
The Origins of NFTs
The concept of NFTs dates back to around 2012 with the advent of colored coins on the Bitcoin blockchain. Colored coins were used to represent real-world assets, such as property or shares, but they were somewhat limited in their capabilities.
The real breakthrough came with the launch of the Ethereum blockchain in 2015, which introduced the concept of smart contracts. These programmable contracts allowed for the creation of more complex digital assets, paving the way for the first true NFTs.
Key Milestones in the Development of NFTs
One of the first significant implementations of NFTs was CryptoPunks, launched by software developers Matt Hall and John Watkinson in 2017. CryptoPunks are 10,000 unique, pixelated characters that live on the Ethereum blockchain. Each Punk is an NFT, and they quickly gained a cult following, becoming digital collectibles.
However, it was the launch of CryptoKitties later in 2017 that really brought NFTs into the mainstream. CryptoKitties are digital cats that can be bought, sold, and bred. Each cat is an NFT with its own unique attributes. The game became so popular that it clogged the Ethereum network, highlighting both the potential and the challenges of NFTs.
The Current State of the NFT Market
Fast forward to today, and the NFT market has exploded. NFTs are being used to represent a wide range of digital assets, including art, music, virtual real estate, and more. High-profile sales, such as Beeple’s digital artwork selling for $69 million, have attracted significant media attention.
| Rank | NFT | Price (in million $) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Beeple Artwork | 69.3 |
| 2 | CryptoPunk #7804 | 7.6 |
| 3 | CryptoPunk #3100 | 7.6 |
| 4 | ‘Crossroads’ by Beeple | 6.6 |
| 5 | ‘First Twitter Tweet’ by Jack Dorsey | 2.9 |
However, the market is also highly volatile, with prices fluctuating wildly. There are also concerns about the environmental impact of NFTs and the potential for scams and market manipulation.
Despite these challenges, many believe that NFTs represent the future of digital ownership and that they have the potential to transform various industries. As the technology continues to evolve, it will be fascinating to see how the history of NFTs continues to unfold.
How Do NFTs Work?

NFTs are a complex blend of technology, art, and economics. To fully understand their potential, it’s essential to grasp how they function. Let’s break down the mechanics of NFTs.
Explanation of Blockchain Technology and Its Role in NFTs
Blockchain Basics
NFTs are built on blockchain technology, the same decentralized, distributed ledger technology that underpins cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. A blockchain is essentially a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions.
Role in NFTs
In the context of NFTs, blockchain technology is used to record the creation and ownership history of each NFT. Each NFT is associated with a unique set of data stored on the blockchain, which includes information about the NFT’s content, the identity of the creator, and the ownership history.
The Process of Creating, Buying, and Selling NFTs
Creating NFTs
Creating an NFT, also known as minting, involves uploading a digital file to an NFT marketplace and creating a new entry on the blockchain that links to that file. This entry includes a unique identifier for the NFT and metadata about the file, such as the creator’s identity and the file’s content.
Buying and Selling NFTs
Buying and selling NFTs is done through NFT marketplaces. When an NFT is bought, a transaction is recorded on the blockchain that transfers ownership of the NFT from the seller to the buyer. The buyer can then hold onto the NFT, display it in a virtual gallery, or sell it to someone else.
The Role of Ethereum and Other Blockchains in the NFT Market
Ethereum’s Role
Ethereum has played a crucial role in the NFT market due to its smart contract capabilities. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They allow for the creation of NFTs and facilitate the buying and selling process.
Other Blockchains
While Ethereum has been the primary blockchain for NFTs, other blockchains have started supporting NFTs as well. These include Binance Smart Chain, Flow, and Tezos. Each of these blockchains has its own unique features and advantages, and the choice of blockchain can depend on factors like transaction fees, energy efficiency, and community support.
Use Cases of NFTs

NFTs have a wide range of applications across various industries. Their unique properties make them suitable for representing ownership of a diverse array of items, both tangible and intangible. Let’s explore some of the most prominent use cases of NFTs.
NFTs in Digital Art
Monetization for Artists
One of the most well-known applications of NFTs is in the world of digital art. Artists can mint their digital artworks as NFTs and sell them directly to collectors, bypassing traditional art market intermediaries. This allows artists to retain more of the profits from their work and reach a global audience.
Ownership and Provenance
NFTs also solve the problem of proving ownership and provenance in the digital art world. Each NFT contains metadata about the artwork, including the identity of the creator and the ownership history of the piece. This information is stored on the blockchain, providing a transparent and tamper-proof record.
NFTs in Gaming
Ownership of In-Game Assets
In the gaming industry, NFTs are used to represent ownership of in-game assets, such as characters, items, and land. This allows players to truly own their in-game assets and trade them on secondary markets.
Play-to-Earn Models
NFTs also enable play-to-earn models, where players can earn NFTs through gameplay and then sell them for real-world money. This has the potential to transform the gaming industry and create new economic opportunities for players.
NFTs in Real Estate and Other Industries
Fractional Ownership
NFTs are being used to represent fractional ownership in real estate, allowing multiple people to invest in properties. Each NFT represents a fraction of the property, and owners can trade their shares on secondary markets.
Proof of Authenticity
In industries such as fashion and luxury goods, NFTs can be used to prove the authenticity of products. Each product can be associated with an NFT, which contains information about its origin, production, and ownership history.
Future Potential Applications of NFTs
The potential applications of NFTs are vast and still being explored. They could be used to represent ownership of intellectual property rights, identity documents, educational credentials, and much more. As the technology matures and becomes more widely adopted, we can expect to see even more innovative uses of NFTs.
The Pros and Cons of NFTs

NFTs have been a game-changer in the digital world, opening up new possibilities for creators and collectors alike. However, like any new technology, they come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s delve deeper into the pros and cons of NFTs.
The Benefits of NFTs
For Creators
NFTs have provided a new platform for artists and creators to monetize their work. They can sell their art directly to consumers, eliminating the need for intermediaries. This has led to artists gaining a larger share of the profits from their work.
For Collectors
For collectors, NFTs offer a new class of digital assets to invest in. They provide a way to prove ownership of a unique piece of content, which can be a valuable asset, especially if the creator becomes more popular over time.
For the Digital Economy
NFTs are also contributing to the growth of the digital economy. They have created a new market for digital assets, leading to increased economic activity in the digital space.
The Challenges and Criticisms of NFTs
Market Volatility
The NFT market is highly volatile, with prices fluctuating wildly. This can lead to significant financial losses for investors who buy at the peak of the market.
Environmental Impact
NFTs have been criticized for their environmental impact. The process of creating and trading NFTs, particularly on the Ethereum blockchain, consumes a large amount of energy, contributing to carbon emissions.
Potential for Scams
The NFT market has also been associated with scams and fraudulent activities. There have been instances of people selling NFTs of artwork that they do not own or have the rights to.
Lack of Regulation
The NFT market is largely unregulated, which can lead to issues such as market manipulation and copyright infringement. There is also a lack of consumer protection in the event of a dispute.
In conclusion, while NFTs offer exciting opportunities, they also come with significant risks and challenges. It’s important for anyone interested in NFTs to do thorough research and understand both the pros and cons before diving in.
How to Get Started with NFTs

Entering the world of NFTs can seem daunting at first, but with a step-by-step approach, you can navigate this exciting digital landscape. Here’s a guide on how to get started with NFTs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Buying Your First NFT
1. Set Up a Digital Wallet
The first step to getting started with NFTs is setting up a digital wallet. This wallet will be used to store your NFTs and the cryptocurrency you’ll use to buy them. Some popular digital wallets include MetaMask, WalletConnect, and Coinbase Wallet.
2. Buy Cryptocurrency
Next, you’ll need to buy some cryptocurrency. Most NFT transactions are done with Ether (ETH), the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum blockchain. You can buy ETH from a cryptocurrency exchange and then transfer it to your digital wallet.
3. Choose an NFT Marketplace
Choosing the right NFT marketplace is a crucial step in your NFT journey. Different marketplaces cater to different types of NFTs and have varying features, fees, and communities. Here are some of the most popular NFT marketplaces:
| Marketplace | Description | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|
| OpenSea | OpenSea is the largest general marketplace for NFTs, offering a wide range of digital assets including art, domain names, virtual world items, and more. | OpenSea supports both Ethereum and Polygon blockchains, offers a user-friendly interface, and has a large and active community. |
| Rarible | Rarible is a creator-centric marketplace that allows anyone to mint, buy, and sell NFTs. | Rarible offers a decentralized platform with its own governance token, RARI, which is distributed to active users. |
| Foundation | Foundation is a marketplace focused on digital art. It operates on an invite-only basis, with artists needing to be invited by the community to mint NFTs. | Foundation has a curated approach, focusing on high-quality digital art. It has been used by several high-profile artists. |
| SuperRare | SuperRare is a marketplace for single-edition digital artworks. Each artwork is minted as a single, unique NFT. | SuperRare focuses on scarcity and exclusivity, with each artwork being one-of-a-kind. |
When choosing a marketplace, consider factors like the types of NFTs available, the user interface, the community, the fees, and the security features. Always do your research and choose a marketplace that aligns with your needs and interests.
4. Buy Your First NFT
Now you’re ready to buy your first NFT! Browse the marketplace, find an NFT you like, and click ‘buy’ or ‘place a bid’. The NFT will be transferred to your digital wallet, and you’ll officially be an NFT owner.
Tips for Choosing a Digital Wallet and NFT Marketplace
Choosing the right digital wallet and marketplace is crucial for a smooth and secure NFT experience. Here are some tips:
1. Security
Look for a wallet and marketplace with strong security features. This includes two-factor authentication, secure login methods, and a good reputation in the community.
2. User Experience
Choose platforms that offer a good user experience. This includes a user-friendly interface, good customer support, and a large and active community.
3. Fees
Be aware of the fees associated with the wallet and marketplace. These can include transaction fees, listing fees, and gas fees on the Ethereum network.
4. NFT Drops Calendar
Consider choosing a marketplace that provides an NFT drops calendar. This can help you stay updated with upcoming NFT releases and plan your purchases accordingly.
Advice for Avoiding Scams and Protecting Your Digital Assets
The world of NFTs is exciting, but it’s also new and relatively unregulated, which means it can be a target for scams. Here are some tips to protect yourself:
1. Do Your Research
Always do your research before buying an NFT. Verify the identity of the creator and the authenticity of the NFT.
2. Be Wary of Too-Good-To-Be-True Deals
If a deal seems too good to be true, it probably is. Be cautious of NFTs being sold for significantly less than their market value.
3. Keep Your Wallet Secure
Never share your wallet’s private keys with anyone, and always use secure and private internet connections when handling your digital assets.
Case Studies of Successful NFTs
The NFT market has seen some remarkable success stories that have helped shape the landscape and perception of NFTs. Let’s delve into a few notable examples.
Beeple’s “Everydays: The First 5000 Days”
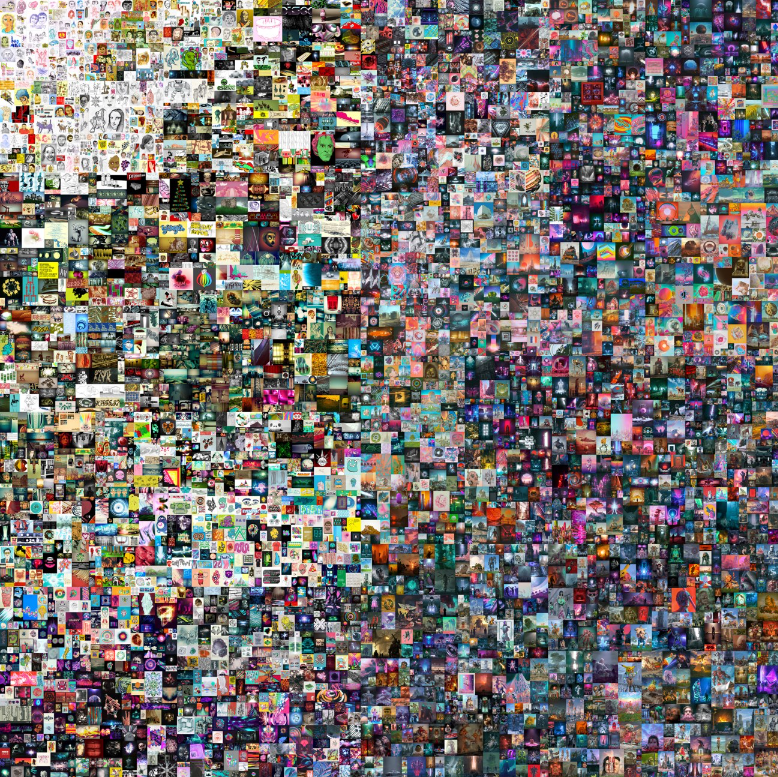

Digital artist Beeple, also known as Mike Winkelmann, made headlines when his NFT artwork, “Everydays: The First 5000 Days,” sold for a staggering $69.3 million at Christie’s auction house. This sale not only set a record for the most expensive NFT ever sold but also positioned Beeple among the top three most valuable living artists.
CryptoPunk #7804

CryptoPunks are one of the earliest examples of NFTs, created by software developers Matt Hall and John Watkinson. These 10,000 unique, pixelated characters have become highly sought after. CryptoPunk #7804, one of the 10,000 unique 24×24 pixel art characters, was sold for 4200 ETH, equivalent to approximately $7.6 million at the time of sale.
Twitter CEO’s First Tweet
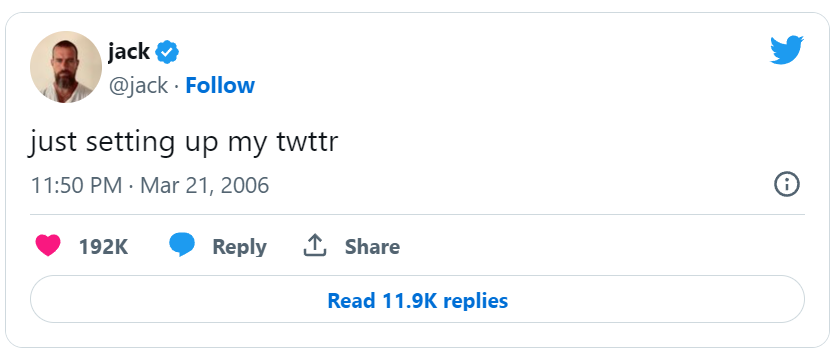
Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey sold his first-ever tweet as an NFT for over $2.9 million. The tweet, which reads “just setting up my twttr,” was published on March 21, 2006, and was sold via the platform Valuables by Cent. The proceeds from the sale were converted to Bitcoin and donated to charity.
Link to Jack Dorsey’s First Tweet
These case studies highlight the diverse range of NFTs and their potential value. They also underscore the importance of uniqueness and provenance in the NFT market.
The Future of NFTs

As we continue to navigate the digital age, NFTs are poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of various industries. Let’s explore some of the potential future directions for NFTs.
Predictions for the Future of the NFT Market
While it’s challenging to predict the future of such a rapidly evolving market, many experts believe that NFTs are here to stay. They foresee NFTs becoming a standard part of the digital economy, particularly in areas like digital art, gaming, and virtual real estate.
Moreover, as blockchain technology continues to mature and become more mainstream, it’s likely that we’ll see more sophisticated and diverse uses of NFTs. For instance, we could see NFTs being used to represent ownership of physical assets, such as cars or houses, or even intangible assets like patents and copyrights.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities for NFTs
Like any emerging technology, NFTs face potential challenges. One of the main concerns is the environmental impact of NFTs, particularly those on the Ethereum blockchain, which currently uses a lot of energy. However, Ethereum is in the process of upgrading to a more energy-efficient system, which could help mitigate this issue.
Another challenge is regulatory uncertainty. As NFTs become more popular, they are likely to attract more attention from regulators. This could lead to new regulations that could impact the NFT market.
On the other hand, NFTs also present significant opportunities. They have the potential to democratize access to wealth and opportunities by allowing anyone to create and sell digital assets. They could also transform industries like art, music, and real estate by providing a new way to prove ownership and monetize digital assets.
How NFTs Could Transform Various Industries
NFTs have the potential to transform various industries. In the art world, they could democratize access to art by allowing artists to sell their work directly to the public. In the music industry, they could provide a new way for musicians to monetize their work and engage with fans. In real estate, they could enable fractional ownership of properties, making real estate investment more accessible.
Furthermore, NFTs could also play a role in the future of work and the gig economy. For instance, freelancers could use NFTs to prove ownership of their work and ensure they are fairly compensated.
Conclusion
As we’ve explored throughout this article, Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) represent a significant shift in the digital landscape. They’ve introduced a new way of proving ownership and monetizing digital assets, opening up a world of possibilities for artists, creators, and collectors alike.
We’ve seen how NFTs have already made a significant impact in areas like digital art, gaming, and virtual real estate. They’ve allowed artists to sell their work directly to consumers, gamers to truly own their in-game assets, and investors to buy and sell shares in properties.
However, as with any new technology, NFTs also come with challenges. The environmental impact, potential for scams, and regulatory uncertainties are all issues that need to be addressed as the NFT market continues to evolve.
Looking ahead, the future of NFTs is full of potential. As blockchain technology continues to mature and become more mainstream, we can expect to see even more innovative uses of NFTs. They could transform various industries, democratize access to wealth and opportunities, and even change the way we work.
In conclusion, whether you’re an artist, a collector, a gamer, or just someone interested in the digital economy, it’s worth keeping an eye on the development of NFTs. They represent a fascinating intersection of art, technology, and economics, and we’re just beginning to scratch the surface of what’s possible. As we continue to navigate this exciting new frontier, one thing is clear: the world of NFTs is a space to watch.
FAQs
What is an NFT?
An NFT, or Non-Fungible Token, is a type of digital asset that represents ownership of a unique item or piece of content, stored on a blockchain.
How do I buy an NFT?
To buy an NFT, you’ll need a digital wallet, some cryptocurrency (usually Ether), and an account on an NFT marketplace.
Are NFTs a good investment?
Like any investment, NFTs come with risks and should be approached with caution. It’s important to do your research and understand the market before investing.
What is the most expensive NFT ever sold?
As of June 2023, the most expensive NFT ever sold is a piece of digital art by Beeple, which sold for $69.3 million.
Can I create my own NFT?
Yes, anyone can create an NFT. All you need is a digital wallet, some Ether, and a connection to an NFT marketplace where you can mint (create) your NFT.
What makes NFTs unique?
NFTs are unique because they represent ownership of a unique item or piece of content. Each NFT has specific information or attributes that make it unique and therefore non-fungible.
Can NFTs be copied?
While the digital content associated with an NFT can be copied, the ownership recorded on the blockchain cannot. Owning an NFT means owning the original item.
What does the future hold for NFTs?
The future of NFTs is still unfolding, but they have the potential to transform various industries by providing a new way to prove ownership and monetize digital assets.
What are some popular NFT marketplaces?
Some popular NFT marketplaces include OpenSea, Rarible, Foundation.


