Blockchain technology, a term that has become synonymous with a new era of digital innovation, is transforming the way we perceive and interact with the digital world. This article aims to demystify blockchain, providing a comprehensive understanding of its origins, workings, and potential applications. So, are you ready to embark on this exciting journey into the future of technology?
Table of Contents
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain: A Definition
Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology that records and verifies transactions across a decentralized network of computers, also known as nodes. The term “blockchain” comes from the way the technology works: transactions are grouped together in blocks, and these blocks are linked together in a chain.
Each block contains a list of transactions, and each time a new transaction occurs on the blockchain, a record of that transaction is added to every participant’s ledger. This decentralized database managed by multiple participants is known as Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT).
Blockchain is structured in such a way that it is resistant to the modification of its data. This is because once information is recorded in a block, it cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks and the consensus of the network majority. This makes blockchain a particularly secure technology and very useful for recording events, medical records, identity management, transaction processing, documenting the provenance of goods, food traceability, and voting systems, among other things.
The blockchain is transparent and incorruptible, and all transactions taking place on the network are verified by a large number of computers (nodes) around the world. These properties make the blockchain secure from fraudulent activities and hacks.
Fast Fact:
Did you know? The first blockchain was conceptualized and implemented as part of Bitcoin in 2009!
The Evolution of Blockchain
The concept of blockchain technology was first introduced in 2009 by an anonymous person (or group of people) known as Satoshi Nakamoto. Satoshi Nakamoto published the Bitcoin whitepaper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System,” which proposed a digital currency, Bitcoin, that would rely on an innovative cryptographic method for secure transactions without the need for a centralized authority.
This was the birth of blockchain technology, with Bitcoin being its first application. The Bitcoin blockchain was designed to track and verify all Bitcoin transactions, ensuring the security and integrity of the digital currency. The decentralized nature of the Bitcoin blockchain solved the double-spending problem (the risk of a digital currency being spent more than once), which had plagued previous attempts at digital currencies.
In 2013, the concept of blockchain took a significant leap forward with the introduction of Ethereum by Vitalik Buterin. Ethereum expanded on Bitcoin’s blockchain technology by introducing smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This opened up a world of possibilities for the use of blockchain technology beyond just cryptocurrency.
Since then, blockchain technology has continued to evolve and has found applications in various industries. It has been used to improve supply chain transparency, secure patient data in healthcare, streamline financial transactions, and much more. The technology has also given rise to new concepts such as decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
The evolution of blockchain technology is still ongoing, with researchers and developers continually exploring new ways to improve scalability, efficiency, and security. As we move forward, it’s clear that blockchain technology will continue to play a significant role in digital innovation.
How Does Blockchain Work? A Simplified Explanation

Blockchain technology operates through a network of computers, also known as nodes, each of which holds a copy of the entire blockchain. Transactions are grouped into blocks, verified by nodes, and added to the chain in a linear, chronological order. This process ensures the integrity and transparency of the data.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the process:
Transaction Initiation
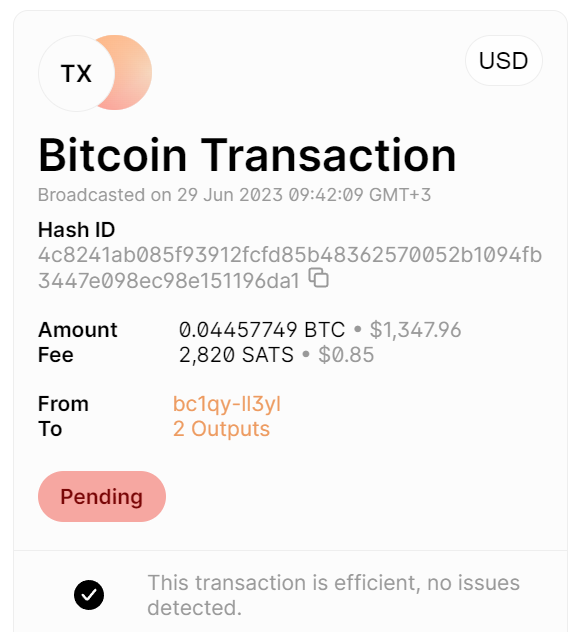
A user initiates a transaction, such as sending cryptocurrency to another user. This transaction is broadcasted to all nodes in the network.
Block Formation
The transaction is grouped with other pending transactions into a block. Each block has a certain capacity, and once this capacity is reached, the block is ready to be added to the blockchain.
Block Verification
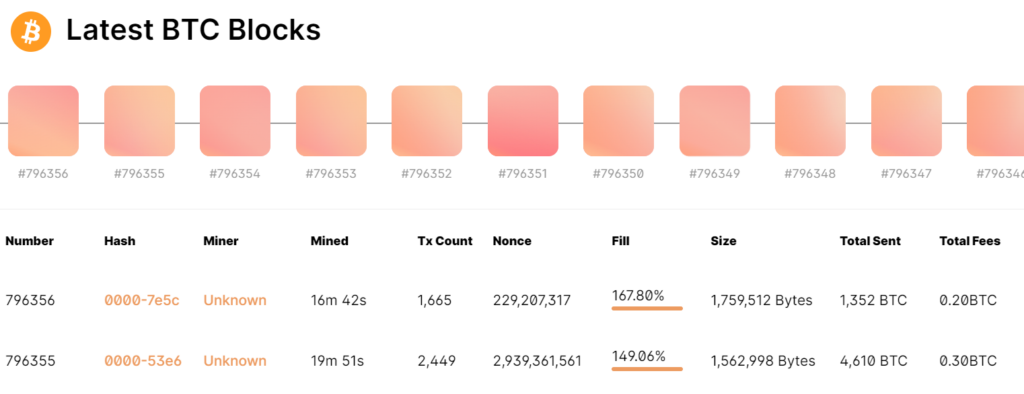
Nodes in the network validate the transactions in the block. This process involves solving complex mathematical problems, also known as proof of work in the case of Bitcoin. The first node to solve the problem broadcasts the solution to the other nodes in the network.
Block Addition
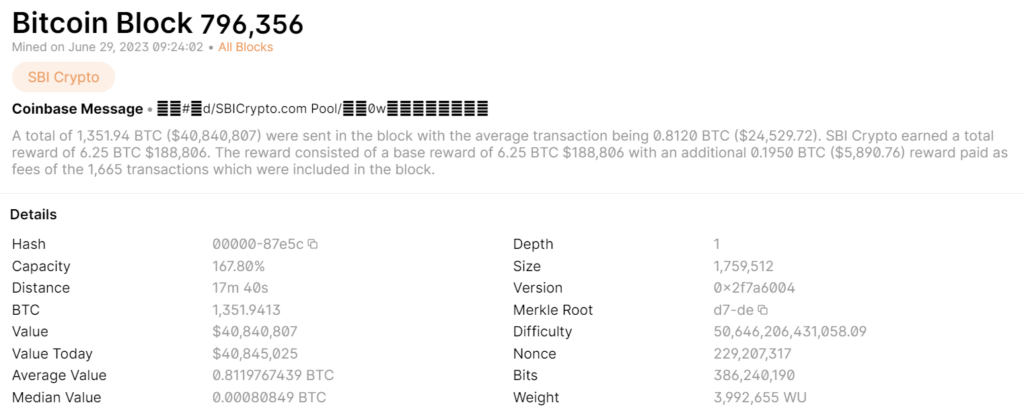
If the majority of nodes agree that the solution is correct (a process known as consensus), the block is added to the blockchain. This block is linked to the previous block using a unique code called a hash. This hash is a function of the contents of the block and the hash of the previous block, creating a chain of blocks, hence the name “blockchain.”
Here’s a flowchart to illustrate the process:
User initiates a transaction –> Transaction is broadcasted to all nodes in the network –> Transaction is grouped with other pending transactions into a block –> Nodes in the network start validating the transactions in the block –> The first node to solve the complex mathematical problem broadcasts the solution to other nodes –> If the majority of nodes agree that the solution is correct, the block is added to the blockchain
And here’s a formula to represent the hashing process:
Hash(Block) = Hash(Transactions, Previous Block's Hash, Timestamp)
In this formula, the hash of a block is a function of the transactions in the block, the hash of the previous block, and a timestamp.
In summary, blockchain works by grouping transactions into blocks, verifying these blocks through a network of nodes, and adding them to a chain of previous transactions. This process ensures the security, transparency, and integrity of the data on the blockchain.
Types of Blockchain

There are primarily three types of blockchain networks: Public Blockchains, Private Blockchains, and Consortium Blockchains. Each type has its own characteristics, uses, and levels of access and control.
Public Blockchains
These are open to anyone who wishes to participate. They are fully decentralized, and no single entity has control over the network. Transactions on these blockchains are transparent, meaning anyone can view the transaction history. Bitcoin and Ethereum are examples of public blockchains. These blockchains are secured by cryptographic algorithms and are consensus-driven, meaning that a majority of participants need to agree on the validity of transactions.
Private Blockchains
These are restricted to specific members, often within a single organization. They are centralized to some extent, with one organization having control over who can join the network, submit transactions, and validate blocks of transactions. Private blockchains are often used by businesses for internal purposes due to their increased efficiency and security. An example of a private blockchain platform is Hyperledger Fabric.
Consortium Blockchains
Also known as federated blockchains, these are semi-private and are controlled by a group of organizations rather than a single one. They offer a balance between the security and privacy of private blockchains and the decentralized nature of public blockchains. Consortium blockchains are often used for business collaborations where multiple organizations need to have input into the network’s operation. An example of a consortium blockchain is Quorum, which is used by a group of major banks to operate the Interbank Information Network.
Each type of blockchain serves different needs and is chosen based on the specific requirements of a use case. For instance, a public blockchain would be suitable for a digital currency like Bitcoin, where transparency and decentralization are essential. In contrast, a private blockchain might be used by a corporation for internal record-keeping, where control and privacy are more important.
Private vs Public Blockchain
| Aspect | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Open to anyone who wishes to participate. | Restricted to specific members, often within a single organization. |
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized, no single entity has control over the network. | Centralized to some extent, with one organization having control over the network. |
| Transparency | Transactions are transparent, meaning anyone can view the transaction history. | Transaction visibility can be controlled and is usually visible only to the participants involved. |
| Consensus Mechanism | Typically uses proof-of-work or proof-of-stake mechanisms which can be resource-intensive. | Can use simpler and less resource-intensive consensus mechanisms. |
| Speed and Efficiency | Due to the large number of participants and complex consensus mechanisms, public blockchains can be slower and less efficient. | Faster and more efficient due to fewer participants and simpler consensus mechanisms. |
| Use Cases | Suitable for applications that require transparency and decentralization, such as cryptocurrencies. | Suitable for business applications where privacy, control, and efficiency are important. |
Key Features of Blockchain
| Feature | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Decentralization | Blockchain operates on a network of computers, eliminating the need for a central authority. | This enhances security and promotes transparency. It also prevents any single entity from having control over the entire network. |
| Transparency | Every transaction on a blockchain is visible to all network participants. | This promotes accountability and trust among participants. It also makes it difficult for fraudulent activities to go unnoticed. |
| Immutability | Once a transaction is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered. | This protects against fraud and tampering. It also provides a verifiable and auditable history of all transactions. |
| Security | Blockchain uses advanced cryptographic techniques to ensure the security of transactions. | This makes it extremely difficult for hackers to compromise the data. It also ensures the integrity and authenticity of transactions. |
| Consensus Mechanisms | Blockchain networks use consensus mechanisms to agree on the validity of transactions. | This prevents fraudulent transactions from being added to the blockchain. It also ensures that all participants agree on the state of the blockchain. |
| Smart Contracts | Blockchain can automate the execution of contracts when certain conditions are met. | This increases efficiency and reduces the need for intermediaries. It also ensures the automatic enforcement of agreements. |
These features make blockchain a powerful tool for a wide range of applications, from financial transactions and supply chain management to decentralized applications (DApps) and beyond.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency

The Blockchain-Cryptocurrency Connection
Blockchain technology and cryptocurrency are deeply intertwined, as the former is the underlying technology that makes the latter possible. A cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual form of currency that uses cryptography for security. The first and most well-known cryptocurrency is Bitcoin, which was created in 2009 by an anonymous person (or group of people) known as Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin was the first application of blockchain technology.
How Blockchain Powers Cryptocurrencies
The blockchain is a decentralized ledger of all transactions across a peer-to-peer network. Using this technology, participants can confirm transactions without the need for a central clearing authority. This allows for transparent, verifiable, and permanent methods of recording data and transactions – properties that are especially useful for cryptocurrencies.
In the context of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain technology records transaction details in blocks, verifies them, and adds them to a chain of similar transactions. This process ensures the security and transparency of cryptocurrency transactions, making it nearly impossible to double-spend or counterfeit the digital currency.
Blockchain Beyond Bitcoin
Beyond Bitcoin, blockchain technology is used in many other cryptocurrencies, including Ethereum, Ripple, and Litecoin, among others. Each of these cryptocurrencies operates on its own underlying blockchain.
Ethereum, for instance, introduced the concept of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. This opened up a world of possibilities for the use of blockchain technology beyond just cryptocurrency, leading to the development of decentralized applications (DApps) and decentralized finance (DeFi).
Applications of Blockchain Beyond Cryptocurrency
| Application | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Supply Chain Management | Blockchain can be used to track and trace the movement of goods, right from their origin to the point of consumption. | This enhances transparency, reduces fraud, and ensures the authenticity of goods. |
| Healthcare | Blockchain can be used to securely store patient data, manage consent for data sharing, and track the provenance of drugs. | This improves data security, enhances patient privacy, and reduces fraud and errors. |
| Real Estate | Blockchain can be used to streamline real estate transactions by reducing paperwork, increasing transparency, and speeding up processes. | This reduces fraud, speeds up transactions, and reduces costs. |
| Voting Systems | Blockchain can be used to create secure, transparent, and tamper-proof voting systems. | This enhances trust in electoral processes, reduces fraud, and ensures the integrity of results. |
| Identity Verification | Blockchain can be used to create secure and immutable identity verification systems. | This reduces identity theft and fraud, and enhances security and privacy. |
| Decentralized Finance (DeFi) | Blockchain is used to create decentralized platforms for financial transactions, removing the need for intermediaries. | This democratizes access to financial services, reduces costs, and enhances financial inclusion. |
These are just a few examples of how blockchain technology can be applied beyond the realm of cryptocurrency. The potential applications of blockchain are vast and continue to grow as more industries recognize the benefits of this innovative technology.
The Future of Blockchain

Emerging Trends in Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology continues to evolve, with new trends and applications emerging regularly. One significant trend is the rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), which aims to democratize finance by removing intermediaries and enabling peer-to-peer financial transactions.
Another trend is the integration of blockchain with other emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI). This integration is expected to lead to more efficient and secure systems.
Government-backed digital currencies or Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are also on the rise, with several countries exploring or already implementing their own digital currencies based on blockchain technology.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
Despite its potential, blockchain technology also faces several challenges. These include scalability issues, regulatory uncertainty, and high energy consumption. However, ongoing research and development are addressing these issues. For instance, new consensus mechanisms are being developed to improve scalability and reduce energy consumption.
The Role of Blockchain in Shaping the Future
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries, from finance and supply chain management to healthcare and education. By providing a secure, transparent, and decentralized method of recording and verifying transactions, blockchain can drive economic growth, enhance efficiency, and promote trust.
In the future, we can expect to see more widespread adoption of blockchain technology, with more businesses and governments recognizing its potential and integrating it into their operations. As blockchain technology continues to evolve and mature, it’s clear that it will play a significant role in shaping our digital future.
Conclusion
Throughout this comprehensive exploration, we’ve journeyed through the intricate landscape of blockchain technology. We began by demystifying the core concept of blockchain and its operational mechanics. We then navigated through the various forms of blockchain – public, private, and consortium – each with its unique attributes and applications.
We’ve underscored the pivotal features of blockchain, such as its decentralized nature, transparency, immutability, and robust security, which collectively contribute to its transformative potential. We’ve also illuminated the integral connection between blockchain and cryptocurrency, demonstrating how blockchain serves as the foundational infrastructure for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Beyond the realm of cryptocurrency, we’ve examined the expansive applications of blockchain across diverse sectors, from supply chain management and healthcare to real estate and voting systems. Lastly, we’ve cast our gaze towards the horizon, discussing the emerging trends, potential hurdles, and the transformative role of blockchain in sculpting our digital future.
Blockchain is far more than just a buzzword. It’s a revolutionary technology that’s reshaping our world. As we continue to uncover its potential, one thing is clear: the blockchain revolution is just beginning. This exploration is a testament to the transformative power of blockchain, and it’s exciting to imagine what the future holds as this technology continues to evolve.
FAQs
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a type of distributed ledger technology that records and verifies transactions across a decentralized network of computers. It’s a transparent, secure, and immutable system of recording information.
What are the different types of blockchain?
There are primarily three types of blockchain: Public, Private, and Consortium. Public blockchains are open to anyone and are fully decentralized. Private blockchains are restricted to specific members and are more centralized. Consortium blockchains are controlled by a group of organizations and offer a balance between the decentralization of public blockchains and the control of private blockchains.
How does blockchain relate to cryptocurrency?
Blockchain is the underlying technology that powers cryptocurrencies. It provides a secure and transparent environment for the recording and verifying of cryptocurrency transactions.
What are some applications of blockchain beyond cryptocurrency?
Blockchain has numerous applications beyond cryptocurrency. It can be used in supply chain management to enhance transparency and traceability, in healthcare to secure patient data, in real estate to streamline transactions, and in voting systems to create secure and transparent systems, among other applications.
How can features of blockchain support sustainability efforts?
Blockchain’s transparency and immutability can support sustainability efforts by providing a secure and verifiable way to track and verify sustainable practices. For example, it can be used to trace the supply chain of a product to ensure it is sustainably sourced.
What sets blockchain solution apart from conventional record-keeping solution?
Unlike conventional record-keeping solutions, blockchain is decentralized, transparent, and immutable. This means that no single entity has control over the entire network, all transactions are visible to all network participants, and once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered.
How does blockchain technology help organizations when sharing data?
Blockchain technology provides a secure and transparent platform for data sharing. It ensures that all data is encrypted and only accessible to authorized parties, and it provides a verifiable audit trail of all data transactions.
How does blockchain support data privacy?
Blockchain supports data privacy through encryption and secure hash functions. Only those with the correct decryption key can access the data, ensuring privacy and security.
What is a blockchain developer?
A blockchain developer is a type of software developer who specializes in developing applications using blockchain technology. This can include developing smart contracts, creating decentralized applications (DApps), and implementing blockchain systems.
What is an advantage of using blockchain technology?
One major advantage of using blockchain technology is its ability to provide a secure, transparent, and decentralized system for recording and verifying transactions. This can enhance trust, reduce fraud, and streamline processes.
What is mining in blockchain?
Mining in blockchain refers to the process of validating and verifying new transactions and adding them to the blockchain. This process involves solving complex mathematical problems and is carried out by nodes known as miners.
What is a smart contract in blockchain?
A smart contract in blockchain is a self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. It automatically executes transactions when predefined conditions are met.


