In the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrency, understanding the concept of “impermanent loss” is crucial. This guide aims to shed light on this complex topic, providing you with the knowledge to navigate the crypto landscape confidently.
Table of Contents
Cryptocurrency and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
The world of finance has been revolutionized by the advent of cryptocurrency and Decentralized Finance (DeFi). These innovations have introduced a new era of financial systems that operate independently of traditional banking institutions.
Understanding Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual form of currency that uses cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by central banks, cryptocurrencies operate on technology called blockchain, which is a decentralized technology spread across many computers that manage and record transactions.
The appeal of cryptocurrencies lies in their potential to act as a store of value and offer low transaction fees, especially for large transactions. They also provide accessibility to financial services for people who are unbanked or underbanked.
Bitcoin, created in 2009, was the first decentralized cryptocurrency, and since then, many other cryptocurrencies have been created, including Ethereum, Ripple, and Litecoin, among others.
Introduction to DeFi
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, is a term that refers to the use of blockchain, cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, and decentralized applications (dApps) to recreate and improve upon traditional financial systems and services.
DeFi applications aim to disrupt the traditional financial world by creating an open-source, permissionless, and transparent financial service ecosystem. They operate without the need for intermediaries, such as banks or brokerages, and are instead built on public blockchains, primarily Ethereum.
Importance of DeFi
DeFi has the potential to democratize finance by removing barriers and reducing costs for providing and accessing financial services. It can provide a range of financial services — from savings and loans, insurance, trading, to even more complex financial instruments — in a transparent, secure, and efficient manner.
Moreover, DeFi has the potential to increase financial inclusivity for people who are currently unbanked or underbanked by providing them with access to financial services via a smartphone and internet connection.
Liquidity Pools and Yield Farming

In the world of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), liquidity pools and yield farming are two key concepts that every investor should understand. They are fundamental to the functioning of many DeFi protocols and can offer lucrative opportunities for earning returns on your crypto assets.
Understanding Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools are smart contracts that contain funds. In essence, they are pools of tokens that are locked in a contract and are used to facilitate trading by providing liquidity. They are the backbone of many DeFi protocols, enabling users to trade tokens directly from the pool rather than from an order book.
When you deposit your tokens into a liquidity pool, you receive liquidity tokens in return. These tokens represent your share of the total pool and can be redeemed for the underlying assets at any time.
Introduction to Yield Farming
Yield farming, also known as liquidity mining, is a method used to earn rewards from your cryptocurrency holdings. In simple terms, it involves lending your funds to others through the magic of computer programs called smart contracts. In return for your service, you earn fees or rewards.
In yield farming, you provide liquidity to a liquidity pool, and in return, you get a reward. This reward may come from fees generated by the underlying DeFi platform, or some other source.
Some yield farming schemes can be quite complex. They involve multiple DeFi platforms, with liquidity providers frequently moving their funds between different pools to maximize their returns.
The Role of Liquidity Providers
Liquidity providers are the participants who deposit their tokens into liquidity pools. They play a crucial role in DeFi by providing the capital that is used to facilitate trading and lending on these platforms.
In return for providing liquidity, they earn fees from the trades that happen in their pool. The fees are usually a percentage of the trading volume, so pools with more liquidity tend to generate more fees.
However, being a liquidity provider is not without risks. One of the main risks is impermanent loss, which can occur when the prices of the tokens in the pool change compared to when they were deposited. This is why understanding impermanent loss is crucial for anyone considering becoming a liquidity provider.
Understanding Impermanent Loss
Impermanent loss is a unique phenomenon that occurs in the realm of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), specifically when you provide liquidity to Automated Market Makers (AMMs) like Uniswap or Balancer.
What is Impermanent Loss?
Impermanent loss is the difference in potential earnings between holding tokens in an AMM and simply holding them in your wallet. It happens when the price of your tokens changes after you deposit them into the liquidity pool. If the price ratio of the tokens in the pool deviates from when you deposited them, you may experience impermanent loss.
How Does Impermanent Loss Occur?
Impermanent loss occurs due to the mechanism of AMMs. In an AMM, the price of tokens is determined by the ratio of the amounts of the two tokens in the pool. When the price of a token in the pool deviates from the price on the market, arbitrageurs will buy low and sell high until the price is balanced. This process changes the ratio of tokens in the pool and leads to impermanent loss for liquidity providers.
Real-World Examples of Impermanent Loss
Let’s consider a real-world example. Suppose you deposit equal values of two tokens (Token A and Token B) into a liquidity pool. If the price of Token A doubles and the price of Token B remains the same, arbitrageurs will buy the cheaper Token A from the pool and sell the more expensive Token A on the market. This process will continue until the price of Token A in the pool matches the market price. As a result, when you withdraw your liquidity, you will receive more of Token B and less of Token A, leading to impermanent loss.
Impermanent Loss is ‘Impermanent’
The term ‘impermanent’ means the loss is not locked in until you withdraw your liquidity. If the prices return to their original state by the time you withdraw, the loss disappears. However, if the prices remain changed, the impermanent loss becomes permanent when you withdraw.
Understanding impermanent loss is crucial for anyone considering becoming a liquidity provider in a DeFi protocol. It’s a risk that should be factored into any decisions about where and when to provide liquidity.
The Math Behind Impermanent Loss

How to Calculate Impermanent Loss
Impermanent loss is a phenomenon that occurs when providing liquidity in an automated market maker (AMM) system, such as Uniswap or Balancer. It happens when the price of your tokens changes compared to when you deposited them in the pool.
The formula for calculating impermanent loss is as follows:
Impermanent Loss = 2 * sqrt(p) / (1+p) - 1Here, ‘p’ is the price ratio of the two tokens from the time of deposit to the time of withdrawal.
It’s important to note that impermanent loss only becomes “permanent” if you withdraw your liquidity from the pool. As long as the liquidity remains in the pool, there’s a chance that the prices could shift back to their original state, and the loss could be erased.
Impermanent Loss Calculator
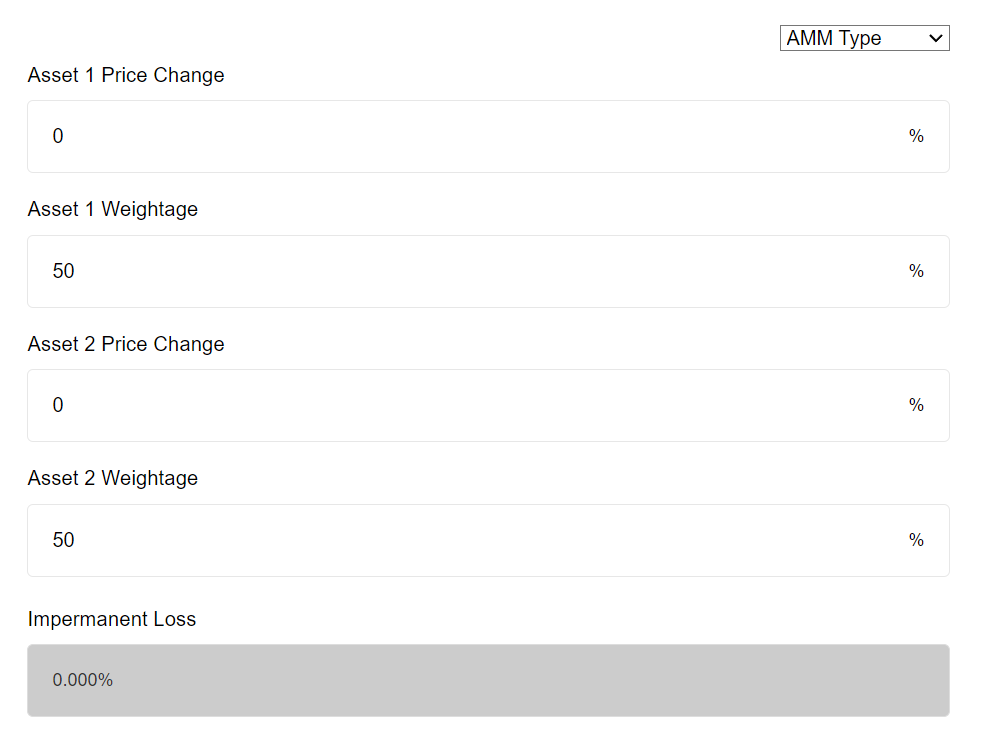
The Impermanent Loss Calculator provided by CoinGecko is a tool designed to estimate the impermanent loss when you provide liquidity to a DeFi protocol. It allows you to enter the weightage of the assets and the expected percentage change to estimate the impermanent loss percentage. It’s important to note that this calculator does not include any trading fees earned, which may help cushion impermanent losses.
How to Use the Impermanent Loss Calculator
Using the Impermanent Loss Calculator is straightforward. You simply input the weightage of the assets in the liquidity pool and the expected percentage change in the price of the assets. The calculator then estimates the percentage of impermanent loss you may experience.
This tool can be particularly useful for liquidity providers who want to understand the potential risks associated with providing liquidity to a particular pool. By estimating the potential impermanent loss, they can make more informed decisions about where and when to provide liquidity.
Limitations of the Impermanent Loss Calculator
While the Impermanent Loss Calculator is a useful tool, it’s important to understand its limitations. The calculator provides an estimate based on the inputs you provide, but it cannot predict future market conditions or price movements. Therefore, the actual impermanent loss you experience may be different from the estimate.
Furthermore, the calculator does not take into account the trading fees earned from providing liquidity, which can help offset impermanent loss. Therefore, while the calculator can provide a useful estimate of potential impermanent loss, it should not be the only tool you use to assess the risks and rewards of providing liquidity.
Examples
Suppose you deposit equal values of two tokens (Token A and Token B) into a liquidity pool. Let’s say the initial price of Token A is $1, and the price of Token B is also $1. Therefore, the price ratio (p) is 1.
Now, let’s say the price of Token A doubles to $2, while the price of Token B remains the same at $1. The new price ratio (p) is now 2.
Substitute p=2 into the formula:
Impermanent Loss = 2 * sqrt(2) / (1+2) – 1 = 0.057 or 5.7%
This means that due to the price change, you would have 5.7% less value compared to if you had just held onto the tokens instead of depositing them into the liquidity pool.
The Impact of Impermanent Loss

Impermanent loss can have significant implications for liquidity providers in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. Understanding its impact is crucial for anyone considering providing liquidity to a DeFi protocol.
How Impermanent Loss Affects Liquidity Providers
Impermanent loss can affect liquidity providers in several ways. The most direct impact is on the potential returns from providing liquidity.
When you deposit your tokens into a liquidity pool, you’re doing so with the expectation of earning returns from trading fees. However, if the prices of the tokens in the pool change significantly, you may experience impermanent loss, which can erode your returns.
In some cases, the impermanent loss can be so significant that it outweighs the returns from trading fees. This means that you would have been better off simply holding onto your tokens rather than depositing them into the liquidity pool.
The Relationship Between Impermanent Loss and Market Volatility
Impermanent loss is closely tied to market volatility. The more volatile the market, the greater the potential for impermanent loss.
In a highly volatile market, the prices of tokens can change rapidly. If the prices of the tokens in a liquidity pool diverge significantly, the impermanent loss can be substantial.
This is why liquidity providers often prefer to provide liquidity to pools with less volatile tokens. Stablecoins, for example, are often used in liquidity pools because their prices are designed to remain stable, reducing the potential for impermanent loss.
Strategies to Mitigate Impermanent Loss

While impermanent loss is a risk inherent to providing liquidity in Automated Market Makers (AMMs), there are strategies that can be used to mitigate its impact. Here are some of them:
Choosing Pools with Less Volatile Tokens
One of the main factors that contribute to impermanent loss is the volatility of the tokens in the pool. The more the prices of the tokens diverge, the greater the potential for impermanent loss. Therefore, one strategy to mitigate impermanent loss is to provide liquidity to pools with less volatile tokens. Stablecoins, for example, are often used in liquidity pools because their prices are designed to remain stable.
Providing Liquidity to Pools with High Volume and Transaction Fees
Another strategy is to provide liquidity to pools with high trading volumes and transaction fees. The fees generated from trades in the pool can offset the potential losses from impermanent loss. However, it’s important to note that pools with high volumes can also experience high price volatility, which can increase the risk of impermanent loss.
Using DeFi Platforms that Offer Impermanent Loss Protection
Some DeFi platforms offer features designed to mitigate impermanent loss. For example, Bancor V2 uses an automated portfolio manager to adjust the weights of the tokens in the pool, which can reduce the potential for impermanent loss. Other platforms offer impermanent loss insurance, which can cover a portion of the potential losses from major price swings.
Balancing Risk and Reward
Ultimately, mitigating impermanent loss involves balancing risk and reward. While providing liquidity can generate returns from trading fees, it also comes with the risk of impermanent loss. Therefore, it’s important to understand the potential risks and rewards, and to make informed decisions based on your risk tolerance and investment goals.
Pros and Cons of Yield Farming Considering Impermanent Loss
Yield farming, also known as liquidity mining, is a popular way to earn rewards by providing liquidity to decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. However, it comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages, especially when considering the risk of impermanent loss.
Here’s a detailed chart that outlines the pros and cons of yield farming, considering impermanent loss:
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Returns | Yield farming can provide substantial returns, especially in pools with high transaction volumes or high reward tokens. | The returns from yield farming can be eroded by impermanent loss, especially in volatile markets. |
| Liquidity | Yield farming contributes to the liquidity of the DeFi market, enabling more efficient trading and price discovery. | If the prices of tokens in a pool diverge significantly, the impermanent loss could exceed the transaction fee income. |
| Diversification | Yield farming allows investors to diversify their portfolio and earn returns from a variety of DeFi protocols. | Yield farming often involves exposure to a variety of tokens, which can increase the complexity and risk of the investment. |
| Innovation | Yield farming is at the forefront of financial innovation, offering new ways to earn returns from crypto assets. | As a relatively new and rapidly evolving field, yield farming comes with risks and uncertainties, including regulatory risks. |
| Accessibility | Yield farming is accessible to anyone with an internet connection and a digital wallet, offering financial opportunities to people around the world. | The complexity of yield farming and the risk of impermanent loss can make it challenging for less experienced investors. |
Balancing the Risk and Reward
It’s essential for yield farmers to understand and balance the potential rewards against the risks. This includes understanding the concept of impermanent loss and how to mitigate it. By doing so, they can make more informed decisions and potentially increase their chances of success in the DeFi space.
Future of DeFi and Impermanent Loss
The future of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and impermanent loss is a topic of great interest to many in the crypto community. As DeFi continues to evolve and mature, we can expect to see new developments and solutions to address the issue of impermanent loss.
How DeFi Protocols are Addressing Impermanent Loss
Many DeFi protocols are actively working on solutions to mitigate impermanent loss. For example, some protocols are developing dynamic automated market makers (AMMs) that adjust the weights of the tokens in the pool based on their price, which can help reduce impermanent loss.
Other protocols are exploring the use of options or insurance-like mechanisms to provide coverage against impermanent loss. These solutions allow liquidity providers to hedge their risk, protecting them from significant losses due to price volatility.
Future Trends and Predictions
As the DeFi space continues to evolve, we can expect to see more sophisticated and effective solutions to impermanent loss. This could include more advanced AMMs, better risk management tools, and more comprehensive insurance options.
Furthermore, as more people become aware of DeFi and start participating in it, there will be an increased demand for education and resources on topics like impermanent loss. This could lead to the development of more user-friendly platforms and tools that make it easier for people to understand and manage the risks associated with providing liquidity in DeFi protocols.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), particularly the concept of impermanent loss, is crucial for anyone looking to venture into the world of cryptocurrency and yield farming. While the potential for high returns is attractive, it’s essential to be aware of the risks involved.
Impermanent loss, a unique phenomenon to liquidity providers in DeFi protocols, can significantly impact your potential earnings. However, with a solid understanding of how it works and strategies to mitigate its effects, you can make more informed decisions about where and when to provide liquidity.
The future of DeFi looks promising, with ongoing innovations aimed at addressing challenges like impermanent loss. As the space continues to evolve, we can expect to see more sophisticated financial products and services, better risk management tools, and more user-friendly interfaces.
In conclusion, while DeFi and yield farming offer exciting opportunities, they also come with their own set of challenges. By staying informed and understanding the risks, you can navigate this landscape more confidently and securely. Remember, in the world of DeFi, knowledge is not just power – it’s profit.
FAQs
What is impermanent loss?
Impermanent loss is the difference between holding tokens in an AMM and holding them in your wallet.
How does impermanent loss work?
Impermanent loss occurs when the price of your tokens changes compared to when you deposited them in the pool.
How can I mitigate impermanent loss?
Strategies to mitigate impermanent loss include choosing pools with less volatile tokens, providing liquidity to pools with high volume and transaction fees, or using DeFi platforms that offer impermanent loss protection.


