In the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrencies, the term “blockDAG coins” has been making waves. But what are they, and why are they gaining such traction? This article delves deep into the world of blockDAG, highlighting its significance and the coins that are leading this revolution.
Table of Contents
What is blockDAG in Crypto?
Historical Context and Evolution
BlockDAG, or Block Directed Acyclic Graph, is a novel approach to the traditional blockchain. While blockchains rely on a linear progression of blocks, blockDAG allows multiple blocks to coexist in parallel, addressing the issue of blockchain’s high orphan rate.
Technical Dive: Understanding DAG
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG) are structures that move in one direction without looping back. In the crypto context, this means transactions can be added without waiting for a previous one to complete, ensuring faster transaction speeds.
Advantages of blockDAG Crypto
BlockDAG, as a novel approach to the traditional blockchain, offers a myriad of advantages that address the limitations of linear blockchains. Here’s a detailed chart highlighting the core advantages of BlockDAG:
| Advantage | Description | Impact on Crypto Ecosystem |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Scalability | BlockDAG allows for the simultaneous addition of multiple blocks, leading to higher transaction throughput. | Can handle a surge in user transactions, making it suitable for mainstream adoption and high-demand applications. |
| Reduced Orphan Rate | The parallel structure reduces the chances of blocks being discarded or becoming ‘orphans’. | Increases the efficiency of the network and ensures that miners’ efforts aren’t wasted. |
| Improved Security | The non-linear structure makes it difficult for attackers to alter the transaction history. | Enhances trust in the system and reduces vulnerabilities to certain types of attacks. |
| Faster Confirmations | Transactions get confirmed faster due to the parallel addition of blocks. | Users experience quicker transaction verifications, enhancing user experience. |
| Decentralization | BlockDAG crypto promotes a more decentralized mining process, reducing the chances of mining centralization. | A more decentralized network is robust against centralized attacks and promotes a fair distribution of rewards. |
| Energy Efficiency | With fewer orphaned blocks, the energy expended on such blocks is saved. | Contributes to a more environmentally friendly crypto mining process. |
| Flexibility | BlockDAG can adapt to varying transaction loads by adjusting the block addition rate. | Ensures the network remains efficient during both high and low transaction periods. |
BlockDAG Coins Spotlight
The crypto landscape has seen the emergence of several coins that leverage the BlockDAG structure. Let’s delve deeper into them:
Kaspa
- Official Website: http://kaspa.org/
- Year of Establishment: 2021
- By Whom: Yonatan Sompolinsky
- General Purpose: To provide a scalable and decentralized cryptocurrency platform that addresses the limitations of traditional blockchains.
- Consensus Mechanism: Proof-of-Work
- Unique Features:
- Future EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) compatibility
- Community-driven approach
- Advanced security protocols
- Main Use Cases:
- Decentralized finance (DeFi) applications
- Smart contract execution
- Peer-to-peer transactions
Taraxa
- Official Website: https://www.taraxa.io/
- Year of Establishment: 2018
- By Whom: Steven Pu and Justin Snapp
- General Purpose: To create a fast, scalable, and EVM-compatible smart contract platform that integrates AI capabilities.
- Consensus Mechanism: Proof-of-Stake
- Unique Features:
- Integration of AI into the blockchain ecosystem
- EVM compatibility, allowing easy deployment of Ethereum dApps
- A diverse range of tools and partnerships
- Main Use Cases:
- AI-powered decentralized social listening & analytics
- Decentralized exchange and automated market-making
- On-chain sensor signals for fractional ownership
Karlsen Coin
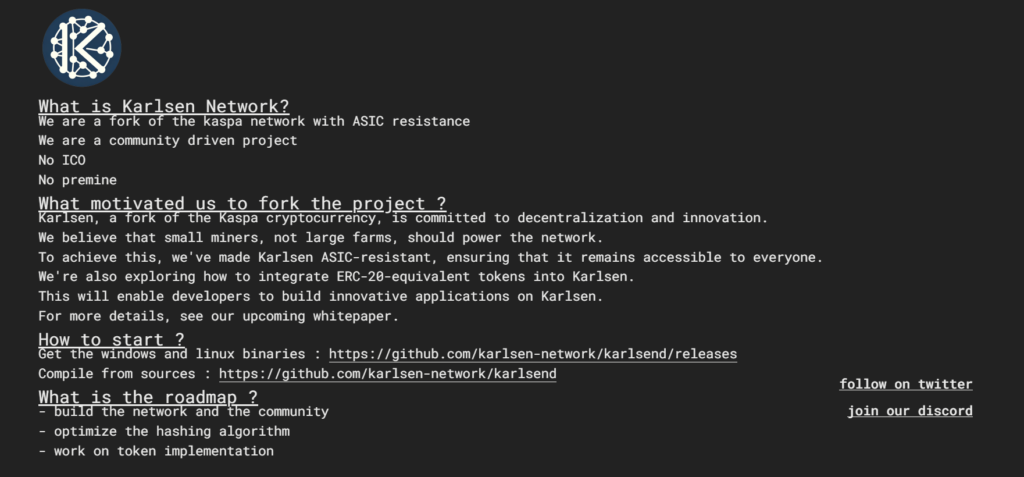
Karlsen Coin emerges as a fork of the Kaspa network, distinguishing itself with a critical feature: ASIC resistance. This design choice underscores its commitment to ensuring mining accessibility, favoring small miners over large industrial-scale farms. By prioritizing a community-driven ethos, Karlsen Coin aligns perfectly with the decentralization spirit inherent in the blockDAG philosophy.
You can buy the coin with MEXC exchange or mine it, by using our “How to Mine Karlsen” guide.
- Official Website: https://karlsencoin.com/
- Year of Establishment: 2023
- General Purpose: To make an ASIC resistant Blockdag project.
- Consensus Mechanism: Proof-of-Work
Other Blockdag Crypto Projects
| Project Name | Website | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrin | pyrin.network | Pyrin aims to offer a new generation transaction network, focusing on decentralization and security for effective and secure transactions. |
| Kaspa Classic | kaspaclassic.com | Utilizes a GhostDAG network for secure, high-throughput, and low-latency transactions, featuring instant confirmations and scalable technology. |
| Sedra Coin | sedracoin.com | A cryptocurrency project that emphasizes eco-friendly mining and secure blockchain technology to support sustainable financial transactions. |
| Hoosat Coin | network.hoosat.fi | Targets enhanced transaction security and scalability, employing cutting-edge blockchain solutions to support efficient digital exchanges. |
Did we overlook something? Send us an email at [email protected].
Comparing blockDAGs and Blockless DAGs
While blockDAGs have their advantages, blockless DAGs like IOTA and Nano bring their unique features to the table. The key difference lies in their structure and transaction speeds.
| Criteria | blockDAGs | Blockless DAGs |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Structure | Incorporate blocks, allowing multiple blocks to coexist in parallel by referencing multiple predecessors. | No blocks. Each transaction references one or more previous transactions, forming a web-like structure. |
| Transaction Speed and Scalability | Achieves higher transaction throughput due to parallel block addition. Suitable for handling a surge in user transactions. | Near-instant transaction confirmations as transactions are added directly without waiting for block formation. |
| Security | Difficult for attackers to alter transaction history due to multiple predecessor referencing. | Direct linking of transactions provides security, but might be more susceptible to certain attacks. Mechanisms are often in place to ensure security. |
Obyte (formerly Byteball) – Example of Blockless DAG
- Year of Establishment: 2016
- By Whom: Tony Churyumoff
- General Purpose: Obyte, previously known as Byteball, is a distributed ledger that aims to achieve true decentralization by eliminating the need for miners and other middlemen. It operates based on a directed acyclic graph (DAG) rather than the traditional blockchain.
- Consensus Mechanism: All Bytes were issued in the Genesis Unit. The total supply of Bytes was created in that and no more can ever be created.
- Unique Features:
- Post-blockchain technology ensuring decentralization without the need for miners.
- Offers conditional payments, P2P prediction markets, and P2P insurance.
- Features like bonded stablecoins, decentralized token registry, and decentralized escrow with arbitration.
- Main Use Cases:
- Decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
- Peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries.
- Cross-chain transfers and prediction markets based on bonding curves.
The Future of blockDAG Coins
The cryptocurrency landscape is in a constant state of evolution, with new technologies and innovations emerging regularly. Among these, blockDAG coins have carved a niche for themselves, promising a future that addresses many of the challenges faced by traditional blockchains. Let’s explore the potential trajectory and implications of blockDAG coins in the coming years.
1. Scalability and Mainstream Adoption
One of the primary challenges for cryptocurrencies has been scalability. As more users join the network, the demand for faster transaction speeds and higher throughput becomes paramount. BlockDAGs, with their ability to process multiple blocks in parallel, are poised to meet this demand. As such, we can anticipate a surge in mainstream adoption of blockDAG coins, especially for applications requiring high transaction volumes, such as e-commerce platforms and financial systems.
2. Enhanced Security Protocols
The unique structure of blockDAGs offers inherent security advantages. However, as with all technologies, there’s always room for improvement. In the future, we can expect the development of even more robust security protocols for blockDAG coins, fortifying them against a wider range of potential attacks and vulnerabilities.
3. Integration with Emerging Technologies
The decentralized nature of blockDAG coins makes them ideal candidates for integration with other emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Decentralized Finance (DeFi). As these technologies continue to evolve, blockDAG coins could play a pivotal role in facilitating seamless, secure, and efficient interactions.
4. Environmental Considerations
With growing concerns about the environmental impact of cryptocurrency mining, blockDAG coins offer a more energy-efficient alternative to traditional proof-of-work systems. As the world moves towards more sustainable practices, blockDAG coins could gain preference for their lower carbon footprint.
5. Diverse Use Cases and Applications
Beyond mere transactions, the future of blockDAG coins lies in their potential to revolutionize various sectors. From supply chain management and transparent governance systems to real-time data sharing in healthcare and entertainment, the applications are vast and varied.
6. Regulatory and Institutional Acceptance
As blockDAG coins gain prominence, they will inevitably attract the attention of regulatory bodies. The future will likely see a more defined regulatory framework for these coins, leading to increased institutional acceptance and investment.
Conclusion
The realm of cryptocurrencies is vast, intricate, and ever-evolving. Within this dynamic landscape, blockDAG coins have emerged as a beacon of innovation, offering solutions to some of the most pressing challenges faced by traditional blockchains. Their unique structure, which allows for parallel processing of blocks, not only addresses issues of scalability but also paves the way for enhanced security and decentralization.
As we’ve delved into the intricacies of blockDAG coins, from their technical underpinnings to their real-world applications, it’s evident that they represent more than just another cryptocurrency. They symbolize a shift in the paradigm, a move towards a more efficient, inclusive, and sustainable digital financial ecosystem.
Kaspa, Taraxa, and Obyte, among others, are not merely coins but flagbearers of this new era. Their diverse features, from AI integration to community-driven approaches, highlight the versatility and potential of blockDAG technology.
Looking ahead, as the world becomes increasingly digital and interconnected, the demand for fast, secure, and scalable financial systems will only grow. In this context, blockDAG coins are poised to play a pivotal role, bridging the gap between current limitations and future possibilities.
In essence, blockDAG coins are not just a fleeting trend but a testament to the spirit of innovation that drives the crypto world. They beckon a future where transactions are swift, systems are secure, and the power of decentralization is harnessed to its fullest. As we stand on the cusp of this exciting future, one thing is certain: blockDAG coins are set to be at the forefront of the next crypto revolution.
FAQs
What are blockDAG coins?
BlockDAG coins are cryptocurrencies that utilize the blockDAG structure instead of the traditional blockchain.
How do blockDAG coins ensure faster transactions?
By allowing multiple blocks to coexist in parallel, blockDAG coins can process more transactions simultaneously.
Are blockDAG coins secure?
Yes, blockDAG coins address the orphan rate problem of blockchains, ensuring a more secure and decentralized network.


