In the dynamic world of crypto trading, the “best stop loss strategy” isn’t just a buzzword—it’s the backbone of successful risk management. With the market’s notorious volatility, having a robust strategy can mean the difference between substantial gains and devastating losses. But what exactly is a stop loss, and how can traders harness its power? Let’s delve in.
Table of Contents
Understanding Stop Loss: The Basics
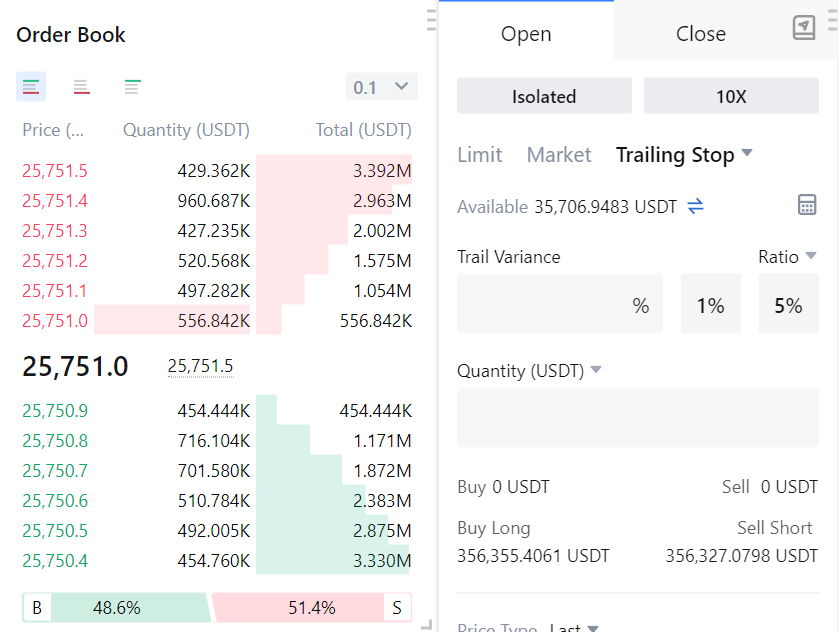
What is a Stop Loss?
A stop loss is a pre-determined order placed with a broker to buy or sell a specific stock once it reaches a particular price. In crypto trading, it’s a safety net, ensuring you don’t lose more than you’re willing to.
Why is Stop Loss Essential in Crypto Trading?
Given the unpredictable nature of cryptocurrencies, a stop loss acts as a protective shield against sudden market downturns, ensuring crypto traders don’t get caught off-guard.
Difference Between Stop Loss and Take Profit
While a stop loss limits potential losses, a take profit order ensures profits are realized before market conditions can reverse.
The Importance of Stop Loss in Crypto Trading
Protecting Your Investment
A well-placed stop loss ensures that you’re not losing more than a predetermined amount, safeguarding your capital from unexpected market swings.
Capitalizing on Market Volatility
By setting strategic stop loss points, traders can leverage crypto market volatility to their advantage, ensuring they exit trades at optimal moments.
Emotional and Psychological Benefits
Trading can be stressful. A stop loss provides peace of mind, knowing there’s a safety mechanism in place.
Different Types of Stop Loss Strategies
Stop loss strategies are crucial in the trading world, especially in the volatile cryptocurrency market. These strategies help traders limit potential losses by automatically selling an asset when it reaches a predetermined price. Let’s delve deeper into the different types of stop loss strategies:
| Criteria | Regular Stop Loss | Trailing Stop Loss | Guaranteed Stop Loss | Time-based Stop Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed price level at which the asset is sold. | Dynamic stop that adjusts with rising market prices but remains static if prices fall. | Sale of assets at the set stop loss level is guaranteed, even in market gaps. | Asset is sold if the desired profit level isn’t achieved within a predetermined timeframe. |
| Usage | Traders with a clear exit price in mind. | Traders wanting to lock in profits during a bullish trend. | Times of high volatility or anticipated significant market news. | When operating based on time-sensitive strategies or avoiding long-term holds. |
| Pros | – Simplicity – Straightforwardness | – Capitalizes on positive market trends – Protection against downturns | – Highest protection against sudden market drops – Avoids market gaps | – Useful for stagnant assets – Time-bound decision making |
| Cons | Market can rebound after hitting stop loss, leading to missed profits. | Rapid fluctuations can trigger the stop prematurely. | – Additional costs – Not available on all platforms | Potential favorable market movement after the time limit. |
| Costs | None (standard trading fees apply). | None (standard trading fees apply). | Premium fee on top of standard trading fees. | None (standard trading fees apply), but potential opportunity costs. |
| Best For | Conservative traders with a set risk threshold. | Active traders in a bullish market. | Traders seeking maximum protection in volatile markets. | Traders with specific time constraints or goals. |
Choosing the Best Stop Loss Strategy

The decision between a Regular Stop Loss and a Trailing Stop Loss is pivotal for traders. Both strategies have their merits and are suited for different trading scenarios. Let’s delve deeper into the intricacies of these two strategies to determine the best stop loss strategy for various situations:
Regular Stop Loss (Fixed Stop Loss)
Definition: A Regular Stop Loss is set at a fixed price level. Once the asset’s price reaches this level, the order is executed, and the asset is sold, preventing further losses.
When to Use:
- When you have a clear idea of the price level at which you’re no longer comfortable holding an asset.
- In markets where you anticipate a significant downturn and want to exit your position before incurring substantial losses.
- When you have a specific target for risk-reward ratio and want to ensure that potential losses do not exceed a predetermined amount.
Advantages:
- Simplicity: It’s straightforward to set up and doesn’t require constant monitoring.
- Predictability: You know the exact price at which your asset will be sold.
Disadvantages:
- Lack of Flexibility: The market can sometimes dip to the stop loss level and then rebound, causing traders to miss out on potential profits.
- No Upside Benefit: Unlike the trailing stop loss, it doesn’t move with favorable market conditions.
Trailing Stop Loss
- Definition: A Trailing Stop Loss is dynamic. It adjusts itself as the market price of the asset rises, ensuring that the stop loss is always a specific distance away from the market price. However, if the market price falls, the stop loss remains static.
When to Use:
- During a bullish market trend where you want to lock in profits without selling your asset too early.
- When you’re unsure about the market’s peak but want to ensure you capture most of the upward movement.
- In markets with strong momentum where prices are steadily rising.
Advantages:
- Profit Maximization: Allows traders to capitalize on positive market movements while still having protection against downturns.
- Dynamic Nature: It adjusts with the market, ensuring you don’t sell too early during a bullish trend.
Disadvantages:
- Premature Sale: Rapid market fluctuations can trigger the stop loss, leading to a sale before a potential rebound.
- Complexity: Requires more active management and monitoring compared to a regular stop loss.
So What Is the Best One?
The best stop loss strategy is subjective and depends on individual trading styles, goals, and market conditions. Both regular and trailing stop losses have their places in a trader’s toolkit, and understanding when to deploy each can significantly impact trading outcomes.
Market Analysis
Understand the current market conditions. If the market is bullish with strong momentum, a trailing stop loss might be more beneficial. In contrast, in a more uncertain or bearish market, a regular stop loss can offer more protection.
Risk Appetite
Traders with a lower risk appetite might prefer the predictability of a regular stop loss, while those willing to take on slightly more risk for potentially higher rewards might lean towards a trailing stop loss.
Trading Goals
If your goal is to protect your capital and minimize losses in a volatile market, a regular stop loss might be more appropriate. However, if you aim to maximize profits during a bullish trend, a trailing stop loss can be more advantageous.
Active Monitoring
If you’re an active trader and can monitor the markets regularly, you might benefit more from the dynamic nature of a trailing stop loss. Passive traders or those who can’t check their portfolios frequently might prefer the set-and-forget nature of a regular stop loss.
Best Stop Loss Strategy Techniques

Best Stop Loss Strategy for Options
Options trading is a complex financial instrument that offers traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on or before a specific date. Given the unique nature of options, implementing an effective stop loss strategy is crucial. Let’s delve into the best stop loss strategy for options:
Understanding the Nature of Options
Before diving into the stop loss strategy, it’s essential to understand the inherent characteristics of options:
- Time Decay (Theta): Options have an expiration date, and their value decreases over time, especially as they approach this date. This phenomenon is known as time decay.
- Intrinsic and Extrinsic Value: The value of an option is composed of its intrinsic value (the difference between the current price of the underlying asset and the strike price of the option) and its extrinsic value (time value + volatility value).
- Volatility (Vega): Options prices are highly sensitive to the volatility of the underlying asset. An increase in volatility can boost the option’s value, while a decrease can diminish it.
Percentage-Based Stop Loss:
- Set a predetermined percentage, say 50%, as your stop loss level. If the option’s value drops by this percentage from your purchase price, sell the option.
- This straightforward approach ensures you only risk a set portion of your investment.
Volatility Stop Loss:
- Given the sensitivity of options to volatility, set your stop loss based on the volatility of the underlying asset. If the asset’s volatility drops significantly, it might be a sign to exit the position.
- Tools like the Average True Range (ATR) can help determine volatility-based stop loss levels.
Time Decay Consideration:
- As the option approaches its expiration date, the time decay accelerates. Consider tightening your stop loss as the expiration date nears to protect against rapid declines in the option’s value.
Hedging with Other Options:
- Instead of using a traditional stop loss, consider hedging your position with another option. For instance, if you own a Call option and want to protect against its decline, you can purchase a Put option on the same asset. This strategy is known as a protective put.
Technical Analysis Stop Loss:
- Use technical analysis on the underlying asset to determine stop loss levels. For instance, if the asset breaks below a significant support level, it might be a sign to sell the option.
Conditional Stop Loss:
- Some advanced trading platforms allow for conditional stop losses. For instance, you can set a stop loss on your option if the underlying asset reaches a specific price or if certain economic indicators hit predefined levels.
Mental Stop Loss:
- Given the rapid price movements in options, sometimes it’s more effective to have a mental stop loss level. Monitor the option’s price and the underlying asset’s performance, and be prepared to sell the option manually when certain conditions are met.
Best Stop Loss Strategy for Intraday / Day Trading
Intraday or day trading involves buying and selling assets within a single trading day, capitalizing on short-term price movements. Given the fast-paced nature of this trading style, having an effective stop loss strategy is paramount. Here’s a detailed look into the best stop loss strategy for intraday or day trading:
Understanding the Nature of Intraday Trading
Before diving into the stop loss strategy, it’s essential to grasp the inherent characteristics of intraday trading:
- Short Time Frame: Trades are opened and closed within a single trading day, which means decisions need to be made quickly.
- High Volatility: Intraday trading often involves assets with significant price fluctuations within short periods.
- Leverage: Many day traders use leverage to amplify their returns, which also increases the potential risk.
Percentage-Based Stop Loss:
- Determine a fixed percentage of your trade as your risk threshold. If the asset’s price moves against your position by this percentage, exit the trade. This approach ensures you’re only risking a set portion of your investment on each trade.
Volatility-Based Stop Loss:
- Use tools like the Average True Range (ATR) to gauge the asset’s typical price fluctuations. Set your stop loss based on a multiple of the ATR, ensuring that you’re accounting for the asset’s inherent volatility.
Support and Resistance Levels:
- Technical analysis can help identify key support (price levels where the asset tends to find buying interest) and resistance (price levels where selling interest typically occurs) levels. Setting stop losses just below support levels or above resistance levels can be effective in intraday trading.
Time-Based Stop Loss:
- Given the short time frame of intraday trading, consider setting a time-based stop loss. If the asset doesn’t move in your favor within a specific timeframe, exit the position. This approach ensures you’re not holding onto non-performing trades for too long.
Trailing Stop Loss:
- As the asset moves in your favor, adjust the stop loss to lock in profits. This dynamic approach ensures that you capture a portion of the gains while still giving the trade room to grow.
Bracket Orders:
- Many trading platforms offer bracket orders, where you can set both a target selling price (take profit) and a stop loss simultaneously. This ensures that you have a clear exit strategy, whether the trade goes in your favor or against it.
Mental Stops vs. Hard Stops:
- While hard stops are automatically triggered by the trading platform, mental stops require manual execution. Given the rapid price movements in intraday trading, it’s often recommended to use hard stops to ensure timely execution.
Additional Considerations
- Stay Informed: Intraday prices can be significantly affected by news events, economic data releases, and market sentiment. Stay updated with real-time news and adjust your stop loss strategy accordingly.
- Review and Adjust: At the end of each trading day, review your trades. Analyze what worked and what didn’t, and adjust your stop loss strategy based on your findings.
- Limit Leverage: While leverage can amplify returns, it also increases risks. Ensure that your stop loss strategy accounts for the added volatility that comes with leveraged positions.
Best Practices for Setting Stop Loss in Crypto

Merely setting a stop loss isn’t enough; it’s vital to do so strategically. Here are some best practices for setting a stop loss in the cryptocurrency market:
1. Analyze Market Conditions:
- Depth: Before setting a stop loss, it’s essential to understand the current market depth, momentum, resistance, and support levels. Technical analysis tools, such as Moving Averages, Bollinger Bands, and Fibonacci retracement, can provide insights into potential price movements.
- Volatility: Cryptocurrencies are known for their volatility. Consider the average volatility of the coin or token when setting your stop loss to avoid getting stopped out during regular price fluctuations.
2. Consider the Coin/Token’s Historical Data:
- Past Performance: While past performance isn’t indicative of future results, analyzing a coin’s historical data can provide insights into its potential volatility and price range.
- Major Support/Resistance Levels: Look for price levels where the cryptocurrency has historically shown strong support (price levels where it tends not to fall below) or resistance (price levels it struggles to surpass). Setting stop losses near these levels can be strategic.
3. Avoid Setting Stop Losses at Obvious Levels:
- Round Numbers: Traders often set stop losses at round numbers (e.g., $10, $50, $100). These levels can become targets for “stop hunters” who intentionally drive the price down to trigger stop loss orders before buying at a lower price.
- Recent Lows: Setting your stop loss right below a recent low can also be predictable. It’s better to give it some buffer to avoid premature selling.
4. Adjust Stop Loss Based on Market News and Updates:
- Stay Informed: Cryptocurrency prices can be significantly affected by news events, such as regulatory changes, technological advancements, or macroeconomic factors. Stay updated with relevant news and adjust your stop loss accordingly.
- React, Don’t Panic: While it’s essential to be responsive, avoid knee-jerk reactions. Analyze how the news might impact the market in the medium to long term before making adjustments.
5. Use Percentage-Based Stop Loss:
- Fixed Percentage: Decide on a fixed percentage (e.g., 5% or 10%) that you’re willing to lose on a trade. This approach ensures that you’re only risking a small portion of your investment, regardless of the coin’s price.
6. Regularly Review and Adjust:
- Dynamic Market: The crypto market is dynamic, and conditions can change rapidly. Regularly review your stop loss settings and adjust them based on new data or market conditions.
- Profit Protection: If your cryptocurrency has gained significantly, consider moving your stop loss up to protect your profits. This strategy ensures that even if the market turns, you’ll still secure a portion of your gains.
7. Factor in Fees:
- Trading Fees: Remember that selling a cryptocurrency, even through a stop loss, often incurs a fee. Ensure that the fee doesn’t significantly erode your capital or profits.
8. Test and Learn:
- Backtesting: Use backtesting tools to test your stop loss strategy against historical data. This practice can give you an idea of how effective your strategy might be in real-world scenarios.
- Continuous Learning: The crypto market is still relatively young and constantly evolving. Always be open to learning and refining your strategy based on new experiences and knowledge.
Common Mistakes to Avoid

When setting a stop loss, especially in the volatile world of crypto trading, there are several pitfalls traders often fall into. Recognizing and avoiding these common mistakes can significantly enhance trading outcomes and protect investments. Here’s a detailed look at these mistakes:
1. Setting Too Tight Stop Losses:
- Pitfall: Some traders set their stop losses extremely close to their entry point, hoping to minimize potential losses.
- Consequence: This can result in the trade being stopped out prematurely due to regular market volatility, even before the price trend truly goes against the trader’s prediction.
- Solution: Give your trades some breathing room. Consider the asset’s average volatility and set a stop loss that allows for normal market fluctuations.
2. Setting Too Wide Stop Losses:
- Pitfall: In fear of getting stopped out, some traders place their stop losses too far from their entry point.
- Consequence: This can lead to larger-than-necessary losses if the market moves unfavorably.
- Solution: Determine a clear risk-reward ratio before entering a trade and set your stop loss accordingly.
3. Not Reviewing or Adjusting Stop Loss:
- Pitfall: Once set, some traders neglect their stop loss, treating it as a “set it and forget it” tool.
- Consequence: As market conditions change, an outdated stop loss can either expose the trader to unnecessary risk or limit potential profits.
- Solution: Regularly review and adjust your stop loss based on new data, market conditions, or changes in your trading strategy.
4. Ignoring Fees Associated with Stop Loss Orders:
- Pitfall: Overlooking the transaction fees that might be incurred when a stop loss order is executed.
- Consequence: The fees can eat into profits or add to losses, especially if trading with a tight margin.
- Solution: Always factor in potential fees when setting a stop loss and ensure that the chosen trading platform offers competitive rates.
5. Relying Solely on Stop Loss Without Other Risk Management Strategies:
- Pitfall: Viewing stop loss as the only necessary tool for risk management.
- Consequence: This narrow approach can expose traders to risks that a stop loss alone can’t mitigate.
- Solution: Combine stop loss with other risk management techniques, such as diversifying your portfolio, setting take profit levels, or using hedging strategies.
6. Setting Stop Losses at Obvious Levels:
- Pitfall: Placing stop losses at predictable levels, such as round numbers or recent highs/lows.
- Consequence: These levels can become targets for “stop hunters” who intentionally drive the price to trigger stop loss orders.
- Solution: Set your stop loss slightly above or below these obvious levels to avoid being targeted.
7. Emotional Decision Making:
- Pitfall: Adjusting or removing a stop loss based on emotions rather than a rational analysis.
- Consequence: Emotional decisions can lead to larger losses or missed profit opportunities.
- Solution: Stick to your trading plan. If you feel the urge to change your stop loss due to emotions, take a step back and re-evaluate the situation objectively.
8. Not Using Stop Loss At All:
- Pitfall: Some traders, especially beginners, might avoid using stop losses altogether, thinking they can manage risks manually.
- Consequence: Without a stop loss, traders are exposed to unlimited downside risk, especially in the volatile crypto market.
- Solution: Always use a stop loss. It’s a fundamental tool for risk management and can protect against sudden and unexpected market downturns.
Advanced Stop Loss Techniques for Seasoned Traders
Seasoned traders often look beyond basic stop loss techniques to optimize their trading strategies. These advanced techniques can provide more flexibility, better risk management, and enhanced profit potential. Let’s delve into some advanced stop loss techniques, keeping in mind the best stop loss strategy practices:
1. Multiple Stop Losses for a Single Position:
- Description: Instead of setting a single stop loss, seasoned traders sometimes split their position into multiple parts, each with its own stop loss level. This allows for a tiered exit strategy.
- Advantage: Provides flexibility in managing a position. If the market reverses after triggering the first stop loss, not all assets are sold, allowing potential recovery and profit from the remaining portion.
2. Moving Stop Loss to Break-Even:
- Description: Once a trade reaches a certain profit level, the stop loss is moved to the entry price. This ensures that, at worst, the trade won’t result in a loss.
- Advantage: Locks in the initial capital, ensuring that even if market conditions change, the trader won’t lose their initial investment.
3. Using Stop Loss in Conjunction with Take Profit:
- Description: Alongside a stop loss, a take profit level is set. This ensures that profits are realized once the asset reaches a predetermined price.
- Advantage: Balances risk and reward. While the stop loss protects against downside risk, the take profit ensures profits are captured during favorable market movements.
4. Algorithmic and Automated Stop Loss Strategies:
- Description: Leveraging algorithms and trading bots to dynamically adjust stop loss levels based on real-time market data and predefined conditions.
- Advantage: Removes emotional decision-making from the process and can react faster to market changes than manual adjustments.
5. Time Decay Stop Loss:
- Description: A stop loss that factors in both price and time. If an asset doesn’t reach a certain price within a specified timeframe, it’s sold.
- Advantage: Useful for traders who operate based on time-sensitive strategies or events. It ensures that capital isn’t tied up in stagnant positions.
6. Volatility-Based Stop Loss:
- Description: The stop loss level is adjusted based on market volatility, often using indicators like the Average True Range (ATR) to determine optimal levels.
- Advantage: Adapts to changing market conditions, ensuring that the stop loss isn’t triggered by regular market noise but only by significant price movements.
7. Combining Stop Loss with Hedging Strategies:
- Description: Using derivatives like futures, options, or other financial instruments to offset potential losses if the stop loss is triggered.
- Advantage: Provides an additional layer of protection. Even if the stop loss results in a sale at a loss, the hedging strategy can compensate for that loss, leading to a net neutral or even positive outcome.
Tools and Platforms for Implementing Best Stop Loss Strategy
Implementing the best stop loss strategy requires not only a deep understanding of market dynamics but also the right tools and platforms to execute these strategies effectively. Here’s a detailed look at some of the top tools and platforms that seasoned traders use to implement their stop loss strategies:
1. Trading Platforms with Advanced Stop Loss Features:
| Platform | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| MEXC | User-friendly interface, wide range of cryptocurrencies, lowest crypto exchange fees, advanced trading features | Platform may be complex for beginners, slow customer service response times |
| Binance | Large number of cryptocurrencies, advanced trading features, high liquidity, user-friendly interface | Reports of delayed customer service responses, potential target for hackers |
| Gate.io | Wide range of cryptocurrencies, advanced trading features, user-friendly interface, educational resources for beginners | Higher trading fees, does not support fiat currency deposits or withdrawals |
| OKX | Large number of cryptocurrencies, advanced trading features, competitive fees, user-friendly interface, educational resources for beginners | Reports of account freezes without prior notice, slow customer service response times |
| BingX | Advanced trading features, high leverage, ability to copy trades from successful traders, user-friendly interface | Smaller selection of cryptocurrencies, less liquidity due to smaller user base |
2. Charting and Analysis Tools:
- TradingView: A favorite among many traders, TradingView offers advanced charting tools, technical analysis, and scripting capabilities. Traders can visualize and plan their stop loss strategies effectively using its intuitive interface.
- CryptoCompare: This platform provides comprehensive cryptocurrency data, charts, and tools, making it easier for traders to analyze market conditions and set appropriate stop loss levels.
3. Mobile Apps for On-the-Go Stop Loss Management:

- Delta: Beyond just portfolio tracking, Delta offers features to set price alerts, which can be used as a manual stop loss reminder when on the move.
- TabTrader: This mobile app aggregates data from most of the popular exchanges, allowing traders to set alerts and execute trades, including stop loss orders, directly from their phones.
4. Automated Trading Bots:
- 3Commas: This platform offers a suite of tools for automated trading, including the ability to set trailing stop losses, which adjust dynamically with the market.
- Cryptohopper: An automated trading bot that allows traders to implement advanced strategies, including various stop loss techniques. Its cloud-based system ensures continuous trading even when the trader’s device is turned off.
- Gunbot: A customizable trading bot that supports multiple exchanges and advanced strategies, including various stop loss techniques.
5. Educational Platforms and Communities:
- BabyPips: While it’s primarily focused on forex trading, BabyPips offers a wealth of information on trading strategies, including stop loss techniques, which can be applied to the crypto market.
- Crypto Trading Communities: Platforms like Reddit, Discord, and Telegram have numerous crypto trading communities where traders discuss strategies, tools, and platforms. Engaging in these communities can provide insights into the latest tools and best practices for stop loss strategies.
Conclusion
In the intricate dance of trading, where market volatility and rapid price shifts are the norm, the best stop loss strategy emerges as a trader’s most trusted partner. It’s the safety net that catches you when market tides turn unexpectedly, ensuring that a bad trade doesn’t escalate into a significant financial setback. Especially in the realm of intraday trading, where decisions are made in the blink of an eye and the room for error is minimal, the importance of a well-crafted stop loss strategy cannot be overstated.
The best stop loss strategy is not just about setting a price point to exit a trade; it’s a holistic approach that considers market volatility, individual risk tolerance, and the broader economic landscape. It’s a dynamic tool, one that evolves with market conditions, trader experience, and the lessons learned from each trade.
In the end, while the markets might be unpredictable, your approach to managing risk doesn’t have to be. By consistently applying and refining the best stop loss strategy tailored to your trading style and goals, you not only protect your investments but also pave the way for sustainable trading success. Remember, in trading, it’s not just about the profits you make, but also about the losses you prevent. And a well-implemented stop loss strategy is the cornerstone of this protective approach.


