In the dynamic world of cryptocurrency, understanding perpetual futures is crucial. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to perpetual futures, their role in the cryptocurrency market, and how they differ from traditional futures.
Table of Contents
What are Perpetual Futures?
Perpetual Futures: A Definition
Perpetual futures, also known as perpetual swaps or crypto perps, are a type of derivative product in the financial market, particularly popular in the cryptocurrency sector. They are similar to traditional futures contracts in that they allow traders to speculate on the future price of an asset. However, there’s a key difference: perpetual futures do not have an expiry date. This means that traders can hold onto these contracts indefinitely, unlike traditional futures that expire on a predetermined date.
The concept of perpetual futures was first introduced in the cryptocurrency market by BitMEX in 2016. It has since become one of the most traded financial instruments in the crypto space due to its unique characteristics.
Perpetual vs. Traditional Futures
Traditional Futures
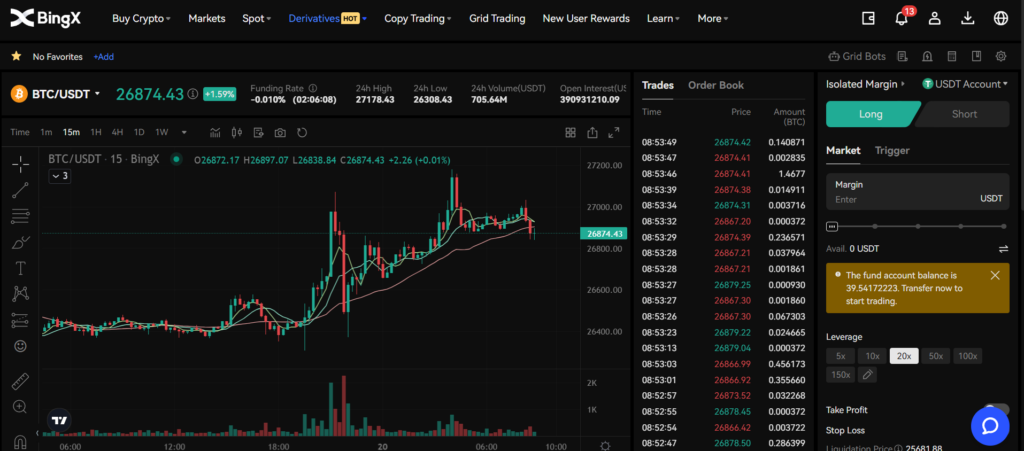
Traditional futures are contracts that obligate the buyer to purchase, and the seller to sell, an asset at a predetermined price and date in the future. These contracts are standardized and traded on regulated exchanges. They are used for a variety of assets, including commodities like oil and gold, financial instruments like bonds and stock indices, and even cryptocurrencies.
One of the key characteristics of traditional futures is their expiration date. When this date arrives, the contract is settled – either by physical delivery of the asset (in the case of commodities) or by cash settlement (in the case of financial instruments). Traders who wish to maintain their position beyond the expiration date must “roll over” their contracts into the next futures contract.
Perpetual Futures
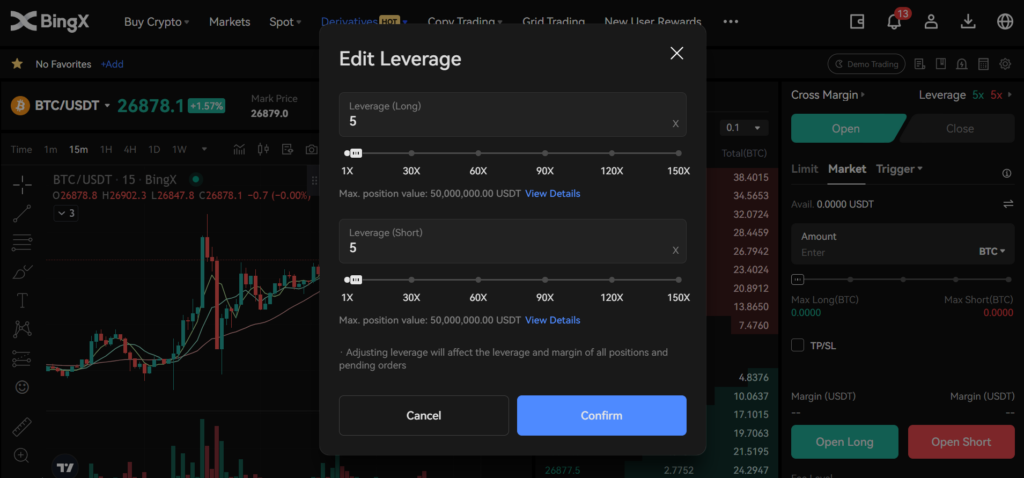
Perpetual futures, on the other hand, are a relatively new type of futures contract that originated in the cryptocurrency market. The key difference between perpetual and traditional futures is that perpetual futures do not have an expiration date. This means traders can hold their position for as long as they want without needing to roll over into a new contract.
Because they have no expiration date, perpetual futures contracts also do not have a delivery date. Instead, they use a mechanism known as “funding rate” to keep the contract price in line with the spot price of the underlying asset. The funding rate is a fee that is paid periodically from one side of the contract to the other, depending on the difference between the contract price and the spot price.
Comparison Chart
| Feature | Perpetual Futures | Traditional Futures |
|---|---|---|
| Expiration Date | No expiration date. Positions can be held indefinitely. | Have a set expiration date. Positions close or need to be rolled over at this time. |
| Settlement | No settlement due to lack of expiry. The contract price is kept in line with the spot price through a “funding rate”. | Settled on the expiration date, either by physical delivery (for commodities) or cash settlement (for financial instruments). |
| Rollover | No need for rollover due to lack of expiry. | Traders who want to keep their position open beyond the expiration date must roll over their contracts. |
| Regulation | Operate in a less regulated environment, as they are a product of the cryptocurrency market. | Traded on regulated exchanges and are subject to regulatory oversight. |
The Role of Perpetual Futures in the Crypto Market

Perpetual futures have become an integral part of the cryptocurrency market due to their unique characteristics and the flexibility they offer to traders. Here are some of the key roles they play:
1. Price Discovery: Perpetual futures contribute significantly to the process of price discovery in the cryptocurrency market. Price discovery is the process by which a market determines the price of an asset. It involves balancing out supply and demand, and in the case of perpetual futures, it’s influenced by factors such as the funding rate and traders’ sentiments about future price movements.
2. Liquidity Provision: Perpetual futures contracts are often highly liquid. This means that large orders can be placed without causing significant price changes, which is beneficial for traders as it allows them to enter and exit positions easily. High liquidity also reduces slippage, which is the difference between the expected price of a trade and the price at which the trade is executed.
3. Hedging Opportunities: Perpetual futures provide traders and investors with a means to hedge their exposure to cryptocurrency assets. For instance, if an investor holds a certain amount of a cryptocurrency and fears that its price may fall in the future, they can short a perpetual futures contract on that cryptocurrency. If the price of the cryptocurrency does indeed fall, the profit from the short position can offset the loss from the spot market, thus providing a hedge against price risk.
4. Leverage Trading: Perpetual futures allow for crypto leverage trading, which means traders can borrow funds to open positions larger than their existing capital. This can potentially lead to higher profits. However, it’s important to note that while leverage can amplify profits, it can also amplify losses.
5. Market Accessibility: Perpetual futures make the cryptocurrency market more accessible. They allow traders to speculate on the price movements of cryptocurrencies without needing to own the actual cryptocurrencies. This can be particularly beneficial in jurisdictions where direct ownership of cryptocurrencies is regulated or restricted.
Perpetual futures play a crucial role in the cryptocurrency market by facilitating price discovery, providing liquidity, enabling hedging, allowing leverage trading, and increasing market accessibility. However, they also come with risks, and traders should have a thorough understanding of these instruments and employ proper risk management strategies when trading them.
How Do Perpetual Futures Work?

The Mechanics of Perpetual Futures
The mechanics of perpetual futures revolve around a few key concepts:
1. Contract and Spot Price: The contract price is the price of the perpetual futures contract, while the spot price is the current market price of the underlying asset. In an ideal scenario, the contract price and spot price should be the same. However, in the real world, these two prices often diverge due to market conditions and traders’ sentiments about future price movements.
2. Funding Rate: To ensure that the contract price stays close to the spot price, perpetual futures use a mechanism known as the “funding rate.” The funding rate is a fee that is paid periodically (usually every 8 hours) from one side of the contract to the other. If the contract price is higher than the spot price (indicating that the market is in a state of “contango”), long contract holders (buyers) pay the funding rate to short contract holders (sellers). Conversely, if the contract price is lower than the spot price (indicating “backwardation”), short contract holders pay the funding rate to long contract holders. This mechanism encourages traders to take the opposite side when the contract price deviates from the spot price, helping to keep the two prices aligned.
3. Leverage: Perpetual futures contracts allow for leverage, meaning traders can borrow funds to open positions larger than their existing capital. This can potentially amplify profits. However, it’s important to note that while leverage can increase profits, it can also amplify losses. If the market moves against a leveraged position, there’s a risk of liquidation, where the position is automatically closed to prevent further losses.
4. Margin and Liquidation: When you open a position with a perpetual futures contract, you need to post a margin, which is a fraction of the total position size. If the market moves against your position and your margin falls below the maintenance margin level, your position will be at risk of liquidation. In the event of liquidation, the exchange will close your position and take the remaining margin.
The Role of Leverage in Perpetual Futures Trading
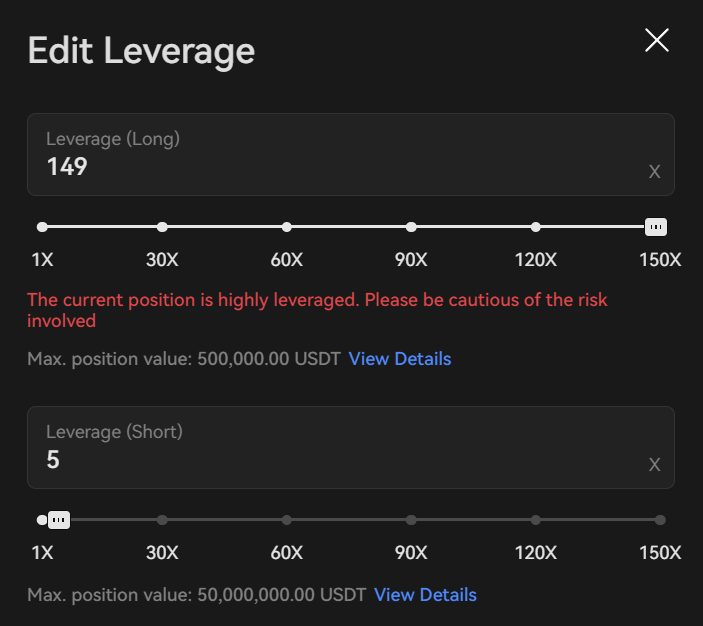
Leverage is a key component of perpetual futures trading. It refers to the use of borrowed funds to increase potential return on investment. In the context of perpetual futures, leverage allows traders to open positions that are larger than the amount of capital they have deposited into their trading account.
Here’s how it works: Let’s say a trader has $1,000 in their account and they want to use 10x leverage to open a position. This means they can open a position worth $10,000, even though they only have $1,000 in their account. The remaining $9,000 is borrowed from the broker or exchange.
The role of leverage in perpetual futures trading is twofold:
1. Amplifying Potential Profits: Leverage can significantly increase the potential profits from a trade. If a trader uses 10x leverage to open a position and the price of the underlying asset moves in the direction they predicted, their profit will be 10 times larger than if they had not used leverage.
2. Increasing Potential Losses: While leverage can amplify profits, it can also amplify losses. If the market moves against the trader’s position, the loss will be 10 times larger than if they had not used leverage. This can lead to the entire margin being lost and the position being liquidated if the market moves significantly against the trader.
It’s also important to note that when trading with leverage, there are often funding costs associated with the borrowed funds. These costs can add up over time, especially for positions that are kept open for long periods.
Leverage plays a crucial role in perpetual futures trading by allowing traders to open larger positions and potentially earn higher profits. However, it also increases the risk of larger losses and can lead to liquidation if not managed carefully. Therefore, it’s essential for traders to understand how leverage works and to use it responsibly.
Benefits of Trading Perpetual Futures

High Returns and Market Accessibility
High Returns
Perpetual futures trading can potentially offer high returns due to the use of leverage. Leverage allows traders to open positions that are significantly larger than their initial capital. For instance, with 10x leverage, a trader can open a position worth $10,000 with just $1,000 in their account. If the market moves in the trader’s favor, the profits can be substantial.
For example, if a trader opens a $10,000 position with 10x leverage and the price of the underlying asset increases by 10%, the trader would make a profit of $1,000 (10% of $10,000), effectively doubling their initial investment. Without leverage, a 10% price increase would have resulted in a profit of only $100 (10% of $1,000).
However, it’s important to note that while leverage can amplify profits, it can also amplify losses. If the market moves against the trader, they could lose a significant portion, or even all, of their initial investment.
Market Accessibility
Perpetual futures also increase market accessibility. They allow traders to speculate on the price movements of cryptocurrencies without needing to own the actual cryptocurrencies. This can be particularly beneficial for traders who want to take advantage of price movements in the cryptocurrency market but do not want to go through the process of buying and securely storing cryptocurrencies.
Moreover, perpetual futures can be traded 24/7, unlike traditional financial markets that have specific trading hours. This allows traders to respond to market events and changes in real-time, regardless of when they occur.
In addition, perpetual futures can be used to trade both long (anticipating price to go up) and short (anticipating price to go down) positions. This means traders can potentially profit from both rising and falling markets.
Flexibility in Trading Strategies

Perpetual futures offer a high degree of flexibility, allowing traders to adapt their strategies based on market conditions and their individual risk tolerance. Here are some of the ways in which perpetual futures provide flexibility:
1. No Expiry Date: Unlike traditional futures, perpetual futures do not have an expiry date. This means traders can hold their positions for as long as they want, without having to worry about the contract expiring. This allows for both short-term and long-term trading strategies.
2. Leverage: Perpetual futures offer leverage, which means traders can open positions that are larger than their available capital. This allows traders to potentially achieve higher returns, although it also increases risk.
3. Long and Short Positions: With perpetual futures, traders can take both long positions (betting that the price will go up) and short positions (betting that the price will go down). This allows traders to profit from both rising and falling markets, and provides opportunities for hedging.
4. Trading Around the Clock: The cryptocurrency market operates 24/7, and so does perpetual futures trading. This means traders can respond to market changes in real-time, no matter when they occur.
5. Variety of Underlying Assets: Perpetual futures are available for a wide range of cryptocurrencies, not just Bitcoin. This allows traders to diversify their portfolio and spread their risk.
Risks Associated with Perpetual Futures

Market Volatility and Perpetual Futures
Market Volatility
Volatility refers to the degree of variation in the price of a financial instrument over a certain period of time. In the context of the cryptocurrency market, volatility is often high due to factors such as regulatory news, technological advancements, market sentiment, and macroeconomic trends. This means the prices of cryptocurrencies can change rapidly in a very short time, making it possible for investors to experience significant gains or losses.
Impact on Perpetual Futures
Market volatility plays a significant role in perpetual futures trading. Here’s how:
1. Profit Opportunities: High volatility can create opportunities for large profits in perpetual futures trading. If a trader can accurately predict the direction of price movement, they can use leverage to amplify their profits. For example, if a trader anticipates that the price of a cryptocurrency will rise, they can go long on a perpetual futures contract. If the price does indeed rise, the trader can make a significant profit.
2. Risk of Losses: On the flip side, high volatility can also lead to large losses. If the market moves against a trader’s position, especially a leveraged one, the losses can be substantial. In extreme cases, a trader could even lose their entire margin and have their position liquidated.
3. Funding Rate Fluctuations: In perpetual futures contracts, the funding rate is used to keep the futures price close to the spot price. During periods of high volatility, the funding rate can fluctuate significantly, which can impact the profits or losses of traders.
4. Increased Trading Activity: High volatility often leads to increased trading activity as traders seek to take advantage of price swings. This can increase the liquidity of perpetual futures contracts, making it easier for traders to enter and exit positions.
The Risk of Liquidation
Liquidation in Perpetual Futures Trading
In perpetual futures trading, liquidation refers to the automatic closure of a position when a trader’s margin balance falls below the maintenance margin level. The margin balance is the amount of money a trader has in their account, while the maintenance margin is the minimum amount that must be maintained to keep a position open.
When a trader uses leverage to open a position in a perpetual futures contract, they are essentially borrowing funds to increase their trading capacity. The initial margin they put up serves as collateral for this borrowed amount.
If the market moves against the trader’s position, their margin balance decreases. If it falls below the maintenance margin level, the exchange will initiate a liquidation process. This means the trader’s position is automatically closed, and the remaining margin, if any, is returned to the trader after deducting any fees.
Risk of Liquidation
The risk of liquidation is one of the most significant risks associated with trading perpetual futures, especially when high leverage is used. High leverage can amplify profits when the market moves in favor of the trader’s position, but it can also amplify losses when the market moves against the position.
In volatile markets, such as the cryptocurrency market, price movements can be swift and significant. If a trader has a highly leveraged position, a relatively small adverse price movement could deplete their margin balance and trigger a liquidation.
Managing Liquidation Risk
To manage the risk of liquidation, traders can employ several strategies:
- Use Lower Leverage: Lower leverage means less borrowing, which reduces the risk of liquidation.
- Set Stop Losses: A stop loss order can automatically close a position once the price reaches a certain level, thereby limiting potential losses.
- Monitor Positions Closely: Traders should keep a close eye on their open positions, especially in volatile market conditions.
- Maintain Adequate Margin Balance: Traders should ensure they have enough funds in their account to maintain their open positions and withstand any adverse price movements.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Trading Perpetual Futures
Step 1: Choose the Right Cryptocurrency Exchange
The first step is to choose a cryptocurrency exchange that offers perpetual futures trading. Some popular exchanges that offer this service include Mexc, Bingx, and OKEx. When choosing an exchange, consider factors such as security, liquidity, trading fees, and the range of available contracts.
Step 2: Set Up a Trading Account
Once you’ve chosen an exchange, you’ll need to set up a trading account. This usually involves providing some personal information and going through a verification process. You’ll also need to secure your account using measures such as two-factor authentication.
Step 3: Deposit Funds
After setting up your account, you’ll need to deposit funds. Most exchanges allow you to fund your account with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or ETH. Some also allow deposits in fiat currency (USDT), depending on the jurisdiction.
Step 4: Understand the Trading Interface
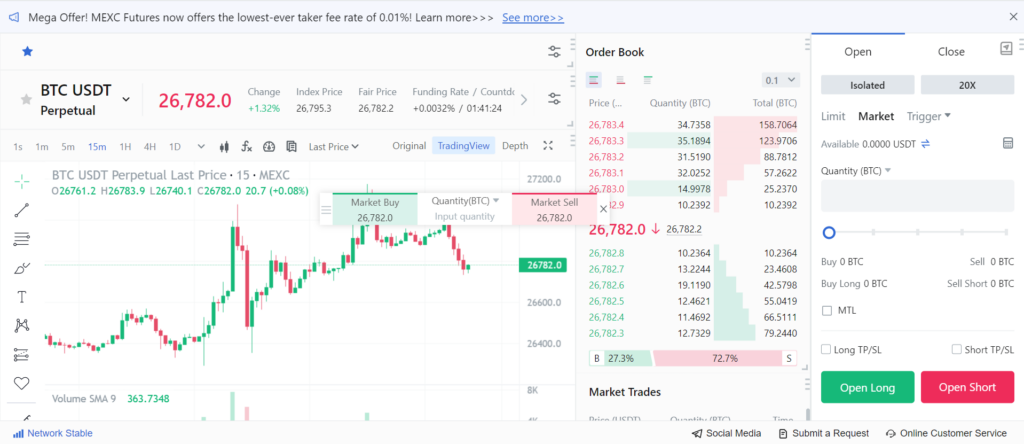
Before you start trading, take some time to understand the trading interface. Familiarize yourself with the order book, price chart, trading pairs, and order types. Most exchanges also provide features like stop-loss orders and leverage settings, which are crucial for risk management in futures trading.
Step 5: Choose a Trading Pair and Contract
Choose the trading pair and the type of contract you want to trade. For example, if you want to trade Bitcoin perpetual futures, you might choose a BTC/USD pair.
BTC Perpetual Futures
Contract and Spot Price: The contract price is the price of the BTC perpetual futures contract, while the spot price is the current market price of Bitcoin. Ideally, the contract price and spot price should be the same, but they often diverge due to market conditions and traders’ sentiments about future price movements.
Funding Rate: To ensure that the contract price stays close to the spot price, BTC perpetual futures use a mechanism known as the “funding rate.” The funding rate is a fee that is paid periodically (usually every 8 hours) from one side of the contract to the other. If the contract price is higher than the spot price, long contract holders (buyers) pay the funding rate to short contract holders (sellers). Conversely, if the contract price is lower than the spot price, short contract holders pay the funding rate to long contract holders. This mechanism encourages traders to take the opposite side when the contract price deviates from the spot price, helping to keep the two prices aligned.
Leverage: BTC perpetual futures allow for leverage, meaning traders can open positions that are larger than their existing capital. This can potentially amplify profits, but it also increases the risk, including the risk of having positions liquidated if the market moves against the trader.
Margin and Liquidation: When you open a position with a BTC perpetual futures contract, you need to post a margin, which is a fraction of the total position size. If the market moves against your position and your margin falls below the maintenance margin level, your position will be at risk of liquidation. In the event of liquidation, the exchange will close your position and take the remaining margin.
Step 6: Decide on a Trading Strategy
Decide whether you want to go long (if you expect the price to rise) or short (if you expect the price to fall). Determine the size of your position and the amount of leverage you want to use. Remember, using high leverage can lead to high profits but also high risk.
Step 7: Place a Trade
Once you’ve decided on your strategy, you can place a trade. Enter the details of your order, such as the contract quantity, order type, and leverage level. Make sure to set a stop-loss order to manage your risk.
Step 8: Monitor Your Trade
After placing your trade, monitor the market and your open position. If the market moves in your favor, you can close your position to take profits. If the market moves against you, your stop-loss order should limit your losses.
Step 9: Close Your Position
You can close your position at any time by placing an order in the opposite direction of your open position. If you’re long, sell the same quantity to close, and if you’re short, buy the same quantity to close.
Best Practices for Trading Perpetual Futures
1. Understand the Basics: Before you start trading perpetual futures, make sure you understand the basics of futures trading and how perpetual futures work. This includes understanding concepts like contract price, spot price, funding rate, leverage, margin, and liquidation.
2. Use Leverage Wisely: Leverage can amplify your profits, but it can also amplify your losses. It’s important to use leverage wisely and not to over-leverage your position. As a rule of thumb, don’t use more leverage than you can afford to lose.
3. Manage Your Risk: Risk management is crucial in perpetual futures trading. This can involve setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, diversifying your trading portfolio, and not investing more than you can afford to lose.
4. Stay Informed: Stay updated with market trends and news. The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile and can be influenced by a variety of factors, including regulatory news, technological advancements, and macroeconomic trends. Staying informed can help you make better trading decisions.
5. Continuous Learning: The cryptocurrency market is constantly evolving, and successful trading requires continuous learning. Make use of educational resources, participate in trading communities, and learn from experienced traders.
6. Practice Discipline: Trading requires discipline. This involves sticking to your trading plan, not letting emotions drive your trading decisions, and knowing when to take profits or cut losses.
7. Use a Reliable Exchange: Choose a reliable cryptocurrency exchange for trading perpetual futures. Consider factors like security, liquidity, trading fees, and the range of available contracts.
8. Regularly Monitor Your Positions: Perpetual futures positions should be monitored regularly, especially in volatile market conditions. This can help you react quickly to market changes and manage your risk effectively.
9. Understand Tax Implications: Trading perpetual futures can have tax implications. It’s important to understand these implications and to keep accurate records of your trades for tax purposes.
10. Seek Professional Advice: If you’re new to trading or if you’re not fully confident in your trading skills, consider seeking advice from financial professionals or experienced traders.
Conclusion
Perpetual futures have emerged as a powerful financial instrument in the cryptocurrency market, offering traders the opportunity to speculate on the future price movements of cryptocurrencies without the need to own the underlying asset. They provide a high degree of flexibility, allowing for both short and long positions, and can be traded with leverage to potentially amplify profits.
However, trading perpetual futures is not without its risks. The cryptocurrency market is known for its volatility, and price swings can be swift and significant. This, coupled with the use of leverage, can lead to substantial losses and even the liquidation of positions if the market moves against a trader.
Therefore, it’s crucial for anyone considering trading perpetual futures to have a thorough understanding of how these instruments work and to employ effective risk management strategies. This includes using leverage wisely, setting stop-loss orders, staying informed about market trends and news, and continuously learning and improving their trading skills.
Moreover, choosing a reliable cryptocurrency exchange, understanding the tax implications of trading, and seeking professional advice can also contribute to a more successful and safer trading experience.
In conclusion, while perpetual futures offer significant potential rewards, they also come with substantial risks. As with any form of trading, they should be approached with caution, knowledge, and a well-thought-out trading plan.
What are perpetual futures?
Perpetual futures, also known as perpetual swaps, are a type of derivative contract primarily used in the cryptocurrency market. They allow traders to speculate on the future price of an asset. Unlike traditional futures, perpetual futures do not have an expiry date, meaning traders can hold onto these contracts indefinitely.
How do perpetual futures work?
Perpetual futures work by allowing traders to buy or sell a contract that represents a certain amount of a specific asset. The price of the contract is kept in line with the spot price of the underlying asset through a mechanism known as the “funding rate.” Traders can also use leverage to open positions larger than their existing capital.
What is the funding rate in perpetual futures?
The funding rate is a fee that is paid periodically (usually every 8 hours) from one side of the contract to the other. It’s used to keep the price of the perpetual futures contract close to the spot price of the underlying asset. If the contract price is higher than the spot price, long contract holders (buyers) pay the funding rate to short contract holders (sellers), and vice versa.
What is leverage in perpetual futures trading?
Leverage in perpetual futures trading refers to the use of borrowed funds to open positions larger than the trader’s existing capital. This can potentially amplify profits, but it also increases the risk of larger losses and liquidation.
What is liquidation in perpetual futures trading?
Liquidation in perpetual futures trading refers to the automatic closure of a position when a trader’s margin balance falls below the maintenance margin level. If the market moves against a leveraged position, there’s a risk of liquidation, where the position is automatically closed to prevent further losses.
How can I manage risk in perpetual futures trading?
Risk in perpetual futures trading can be managed through various strategies, including using leverage wisely, setting stop-loss orders, diversifying your trading portfolio, staying informed about market trends and news, and continuously learning and improving your trading skills.


