Bitcoin mining is a crucial process that underpins the entire Bitcoin network. It involves solving complex cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions and secure the network. In return, miners are rewarded with newly minted bitcoins. But how does it all work, and is it still profitable in 2025? Let’s dive in!
What is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining is a decentralized process that plays a crucial role in the functioning of the Bitcoin network. It involves the use of computer hardware to perform complex calculations, known as proof-of-work, which serve to secure the network and validate transactions. This process is essential for the creation of new bitcoins and the maintenance of the blockchain, a public ledger that records all Bitcoin transactions.
At its core, Bitcoin mining is a competition among miners to solve a cryptographic puzzle. The puzzle is based on the contents of a block of transactions, and the first miner to solve it gets to add the block to the blockchain. This process is known as “finding a block” or “solving a block.” The miner who successfully adds a block to the blockchain is rewarded with newly minted bitcoins, as well as transaction fees from the transactions included in the block.
The mining process serves two primary purposes:
- Issuance of New Bitcoins: The Bitcoin protocol is designed to release a fixed amount of new bitcoins into circulation as a reward for miners who successfully add a block to the blockchain. This is the only way new bitcoins are created, and it ensures a controlled and predictable supply of the cryptocurrency.
- Securing the Network: Mining provides security to the Bitcoin network by making it computationally difficult to alter the blockchain. Once a block is added to the blockchain, it becomes extremely challenging to modify it without redoing the proof-of-work for that block and all subsequent blocks. This ensures the integrity and immutability of the blockchain, making it resistant to fraud and tampering.
Bitcoin mining is a dynamic and competitive process, with miners constantly upgrading their hardware and optimizing their operations to increase their chances of solving a block. The difficulty of the cryptographic puzzles adjusts approximately every two weeks to ensure that blocks are added to the blockchain approximately every ten minutes, regardless of the total computational power of the network.
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
Bitcoin mining is a complex process that involves solving cryptographic puzzles to validate and secure transactions on the Bitcoin network. This process is essential for maintaining the integrity of the blockchain, a public ledger that records all Bitcoin transactions. Let’s break down the key components of Bitcoin mining:
Cryptographic Puzzles
The heart of Bitcoin mining lies in solving cryptographic puzzles, which are mathematical problems designed to be computationally difficult to solve but easy to verify once a solution is found. These puzzles are based on the contents of a block of transactions, and the first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add the block to the blockchain.
Proof-of-Work (PoW) Mechanism
The process of solving cryptographic puzzles is known as proof-of-work. It requires miners to expend computational power to find a solution, which serves as proof that they have invested resources in securing the network. The PoW mechanism is designed to deter malicious actors from attacking the network, as it would be prohibitively expensive to do so.
Block Validation
Once a miner solves a puzzle, they broadcast the solution to the rest of the network for verification. Other miners check the solution and the contents of the proposed block to ensure its validity. If the majority of miners agree that the solution is correct and the block is valid, it is added to the blockchain.
Mining Rewards
The miner who successfully adds a block to the blockchain is rewarded with newly minted bitcoins, known as the “block reward,” as well as transaction fees from the transactions included in the block. The block reward serves as an incentive for miners to invest resources in securing the network and validating transactions.
Difficulty Adjustment
The Bitcoin network adjusts the difficulty of the cryptographic puzzles approximately every two weeks to ensure that blocks are added to the blockchain approximately every ten minutes, regardless of the total computational power of the network. This adjustment helps maintain a stable and predictable rate of block creation.
Consensus Mechanism
Bitcoin mining operates on a consensus mechanism, meaning that all participants in the network must agree on the state of the blockchain. This consensus is achieved through the PoW mechanism, which ensures that only valid blocks are added to the blockchain and that any attempts to alter the blockchain are computationally infeasible.
In summary, Bitcoin mining is a decentralized process that involves solving cryptographic puzzles to validate and secure transactions on the Bitcoin network. Miners compete to solve these puzzles, and the first to succeed gets to add a block to the blockchain and earn rewards in the form of new bitcoins and transaction fees. The process is designed to be computationally intensive, ensuring the security and integrity of the blockchain.
Bitcoin Mining Hardware
Bitcoin mining is a highly competitive and resource-intensive process. Miners need to solve complex cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add the next block and is rewarded with newly minted Bitcoins. This process requires a lot of computational power.
In the early days of Bitcoin, mining could be done using a regular CPU (Central Processing Unit) found in most personal computers. However, as the difficulty of mining increased, CPUs became too slow to be profitable. Miners then started using GPUs (Graphics Processing Units), which are much more powerful than CPUs and are used in gaming computers. GPUs can process multiple calculations simultaneously, making them more suitable for the parallel processing required in mining.
However, even GPUs became insufficient as the mining difficulty continued to rise. This led to the development of ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) for Bitcoin mining. ASICs are custom-designed chips optimized for a specific application—in this case, Bitcoin mining. They are much more powerful and efficient than both CPUs and GPUs.
ASIC miners can perform many terahashes per second (TH/s), whereas a CPU or GPU can only perform a few megahashes or gigahashes per second (MH/s or GH/s). This makes ASICs the preferred choice for Bitcoin mining, as they offer a significant advantage in terms of speed and energy efficiency.
Here are some of the most famous Bitcoin mining hardware producers:
Bitmain
Bitmain is a Beijing-based company that produces the AntMiner line of Bitcoin miners. Bitmain is one of the most well-known and established companies in the Bitcoin mining industry. They also operate a mining pool.
MicroBT
MicroBT is a Chinese ASIC miner manufacturer based out of Shenzhen. Their WhatsMiner series is a major competitor to Bitmain’s AntMiner line. MicroBT’s WhatsMiner M30S+ and M30S++ are known for their high hash rate and efficiency.
Canaan
Canaan is the company that put the very first commercial Bitcoin ASIC miner to market. They produce the AvalonMiner series of Bitcoin miners. Canaan also offers a suite of blockchain tools and business solutions.
Here is a detailed chart comparing some of the most famous Bitcoin mining hardware:
| Manufacturer | Model | Hash Rate | Price Range | Power Consumption | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bitmain | Antminer S19 | 95.0 TH/s | $10k-12k | 3250W | 34.21 J/TH |
| Bitmain | Antminer S19 Pro | 110.0 TH/s | $15k-17k | 3250W | 29.55 J/TH |
| MicroBT | WhatsMiner M30S+ | 100.0 TH/s | $8,500 | 3472W | 34.72 J/TH |
| MicroBT | WhatsMiner M30S++ | 112.0 TH/s | $3,250 | 3472W | 31.00 J/TH |
| Canaan | AvalonMiner 1246 | 90.0 TH/s | $5,500 | 3420W | 38.00 J/TH |
Bitcoin Mining Software
Bitcoin mining software plays a crucial role in the mining process. It connects the mining hardware to the Bitcoin network, manages the mining process, and provides miners with important information such as hash rate, temperature, and mining performance. There are two main types of mining software: ASIC firmware and special monitoring operating systems.
ASIC Firmware
ASIC firmware is software that is specifically designed for ASIC miners. It is installed directly on the ASIC miner and controls the operation of the hardware. ASIC firmware is optimized for mining performance and efficiency. It provides features such as overclocking, underclocking, and voltage control, allowing miners to fine-tune their hardware for optimal performance. Some ASIC manufacturers provide their own firmware, while others rely on third-party firmware.
Luxor Firmware

Luxor is an US company that offers custom firmware for ASIC miners. Their firmware is designed to optimize mining performance, reduce power consumption, and increase the lifespan of the hardware. Luxor firmware also includes features such as auto-tuning, temperature control, and advanced monitoring.
Special Monitoring Operating Systems
Special monitoring operating systems are software platforms that provide a user-friendly interface for managing and monitoring mining operations. These operating systems are typically installed on a separate computer or server and connect to the ASIC miners via a network connection. They provide features such as remote access, real-time monitoring, and advanced analytics.
Hiveon ASIC Hub
Hiveon ASIC Hub is a special monitoring operating system designed for ASIC miners. It provides a web-based interface that allows miners to monitor and manage their mining operations from anywhere with an internet connection. Hiveon Hub offers features such as real-time monitoring, advanced analytics, and automatic firmware updates. It also supports a wide range of ASIC miners from different manufacturers.
Mining Pools
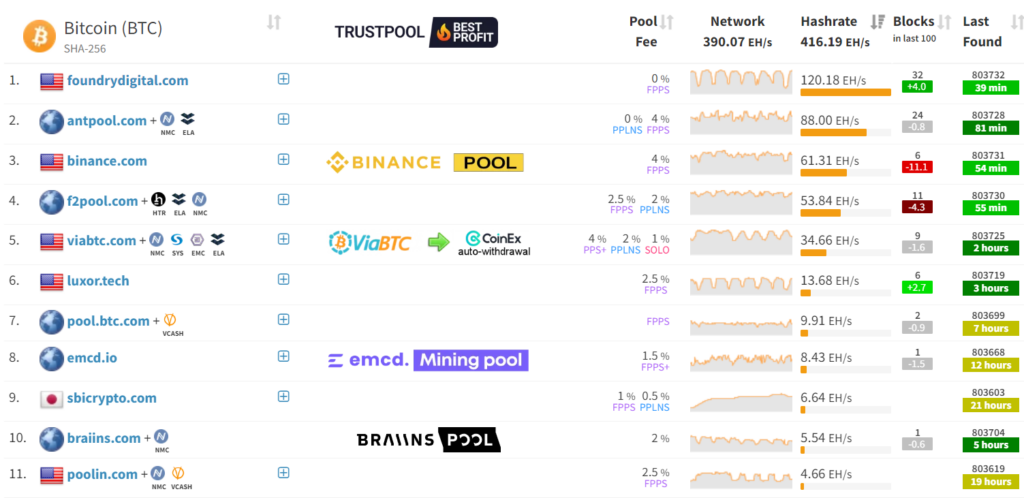
A mining pool is a group of miners who combine their computational power to increase their chances of solving a block and earning Bitcoin rewards. Instead of mining individually, miners join a pool to work together and share the rewards based on their contributed hash power. Mining pools are essential for small-scale miners who may not have enough computational power to mine a block on their own.
Reward Methods
There are several methods that mining pools use to distribute rewards among their members:
- Pay-Per-Share (PPS): In the PPS method, miners are paid for every share they submit, regardless of whether the pool finds a block or not. The pool operator takes on the risk of variance in block finding and pays miners a fixed amount per share. This method provides a steady income for miners.
- Pay-Per-Last-N-Shares (PPLNS): PPLNS is similar to PROP, but it only considers the last N shares submitted by miners. This method discourages pool-hopping and rewards loyal miners who stay with the pool.
Payouts
Mining pools offer different payout options for their members:
- Automatic Payouts: Some pools automatically send payouts to miners once they reach a certain threshold. This option is convenient for miners who want to receive their earnings regularly.
- Manual Payouts: Some pools allow miners to request payouts manually. This option gives miners more control over when they receive their earnings.
- Daily/Weekly/Monthly Payouts: Some pools offer daily, weekly, or monthly payouts, regardless of the amount earned. This option provides a predictable income for miners.
Other Considerations
- Pool Fees: Most mining pools charge a fee for their services. The fee is usually a percentage of the miner’s earnings and is used to cover the pool’s operating costs.
- Minimum Payout Threshold: Some pools have a minimum payout threshold that miners must reach before they can receive their earnings. This threshold helps reduce transaction fees and ensures that miners receive a significant amount.
- Pool Size: The size of the pool affects the frequency of block finding and the variance in earnings. Larger pools find blocks more frequently but have more members to share the rewards with. Smaller pools find blocks less frequently but have fewer members to share the rewards with.
- Pool Reputation: It’s essential to choose a reputable pool with a history of fair payouts and transparent operations. Some pools have been accused of cheating or withholding payments from their members.
Solo Mining vs. Pool Mining
Solo mining and pool mining are two different approaches to earning rewards from cryptocurrency mining. Here’s an elaboration on both methods:
Solo Mining
Solo mining is the process of mining cryptocurrencies independently, without joining a mining pool. In solo mining, a miner attempts to confirm blocks of transactions on the blockchain alone. The miner competes against other nodes and miners to confirm the block of transactions first. This process is called solo mining because the miner is attempting to confirm blocks by mining by himself, without the help of others (pools).
Advantages of Solo Mining:
- Full Rewards: If a solo miner successfully mines a block, they receive the entire block reward and transaction fees. There are no fees to pay to a pool operator.
- No Pool Downtime: Solo miners are not affected by pool downtime or server issues, as they mine independently.
Disadvantages of Solo Mining:
- High Variance: Solo mining is highly dependent on luck. The probability of finding a block as a solo miner is low, and rewards are infrequent and unpredictable.
- Resource-Intensive: Solo mining requires significant computational power to compete with large mining pools. Miners with limited resources may struggle to mine blocks successfully.
Pool Mining
Pool mining is the process of joining a group of miners to combine computational power and work together to mine blocks. In pool mining, miners share their hash power with the pool and work together to find blocks. When the pool successfully mines a block, the rewards are distributed among the miners based on their contributed hash power.
Advantages of Pool Mining:
- Steady Income: Pool mining provides a more steady and predictable income, as rewards are distributed more frequently among pool members.
- Lower Variance: Pool mining reduces the variance in earnings, as miners share the rewards based on their contributed hash power.
- Suitable for Small Miners: Pool mining is suitable for miners with limited resources, as they can join a pool and contribute their hash power to increase their chances of earning rewards.
Disadvantages of Pool Mining:
- Pool Fees: Most mining pools charge a fee for their services, which reduces the miner’s earnings.
- Centralization: Pool mining can lead to centralization, as a few large pools may control a significant portion of the network’s hash power.
Solo Mining Probability
Solo mining nowadays is very dependent on the luck factor. Some people try to mine Bitcoin with only one ASIC machine, but they also have the opportunity to confirm the block and catch an astonishing 6.25 BTC reward! The probability of finding a block vastly depends on the amount of hashrate a solo miner uses for mining.
For example, an AntMiner S19 XP with a speed of 140 TH/s has a 0.000065% chance of catching a block every 10 minutes, given the current Bitcoin network hashrate of 215,370,000 TH/s. Statistically, it would catch a block every 1538357 blocks or 10683 days, which equals to 29 years.
Bitcoin Mining Profitability
Bitcoin mining profitability is a crucial factor for miners to consider before investing in mining hardware and operations. Profitability depends on various factors, including the cost of electricity, the price of Bitcoin, the difficulty of mining, and the efficiency of the mining hardware.
Here are the key factors that affect Bitcoin mining profitability:
Mining Difficulty
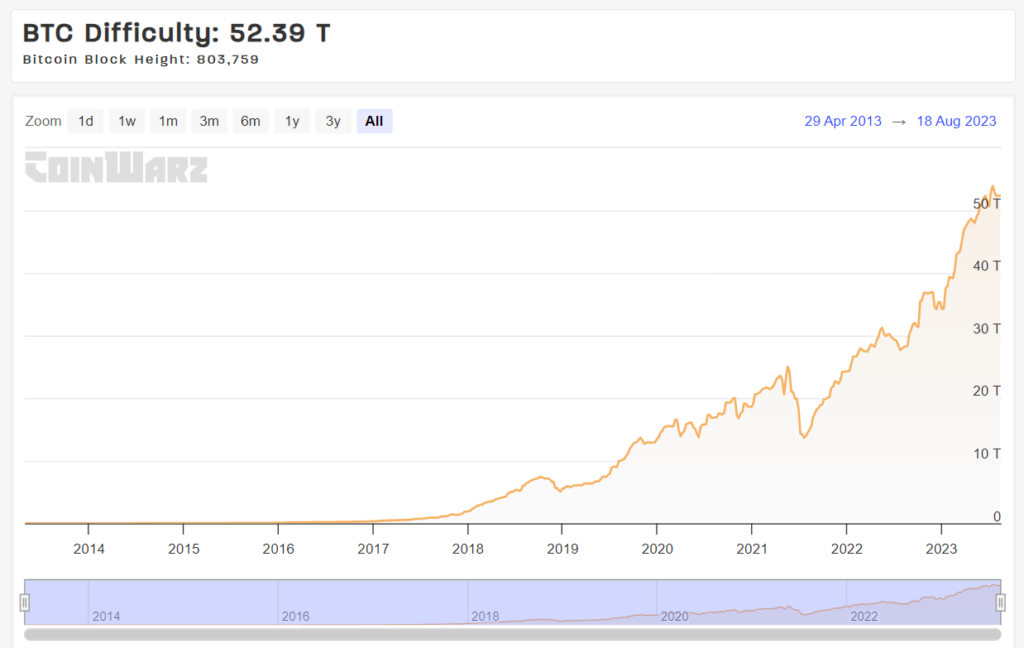
Mining difficulty is a measure of how hard it is to find a new block. It adjusts approximately every two weeks to ensure that blocks are added to the blockchain approximately every ten minutes. As more miners join the network, the difficulty increases, making it harder to mine blocks and reducing profitability.
Block Rewards
Miners are rewarded with newly minted bitcoins and transaction fees for successfully adding a block to the blockchain. The block reward started at 50 bitcoins per block and halves approximately every four years. The current block reward is 6.25 bitcoins per block. As the block reward decreases, miners rely more on transaction fees to maintain profitability.
Price of Bitcoin
The price of Bitcoin plays a significant role in mining profitability. If the price of Bitcoin is high, miners can sell their rewards for more fiat currency, increasing their profits. However, if the price of Bitcoin drops, miners may struggle to cover their operating costs.
Electricity Costs
Electricity is one of the most significant expenses for miners. Mining requires a lot of computational power, which consumes a lot of electricity. Miners need to consider the cost of electricity in their area and the efficiency of their mining hardware to determine profitability.
Mining Hardware Efficiency
The efficiency of mining hardware is measured in joules per terahash (J/TH). More efficient hardware consumes less electricity per terahash, reducing operating costs and increasing profitability.
Pool Fees
If miners join a mining pool, they need to consider the pool’s fees. Most pools charge a fee for their services, which reduces the miner’s earnings.
To calculate Bitcoin mining profitability, miners can use online mining calculators. These calculators take into account factors such as mining difficulty, block rewards, price of Bitcoin, electricity costs, mining hardware efficiency, and pool fees to estimate potential profits.
Here are some popular Bitcoin mining calculators:
These calculators allow miners to input their specific parameters, such as electricity costs and mining hardware efficiency, to get a more accurate estimate of their potential profits.
It’s essential to note that Bitcoin mining profitability can be volatile and depends on various factors that can change over time. Miners need to consider their specific circumstances and regularly reassess their profitability to make informed decisions.
Environmental Impact of Bitcoin Mining

Bitcoin mining is a resource-intensive process that requires significant computational power to solve complex cryptographic puzzles and validate transactions on the Bitcoin network. This process consumes a large amount of electricity, which has raised concerns about its environmental impact.
Energy Consumption
Bitcoin mining operations, especially large-scale ones, consume vast amounts of electricity. The energy consumption of the Bitcoin network is often compared to that of entire countries. According to the Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance, the Bitcoin network’s annual electricity consumption is estimated to be around 121.36 TWh, which is comparable to the energy consumption of countries like Argentina or the Netherlands.
Carbon Footprint
The carbon footprint of Bitcoin mining depends on the source of the electricity used. If the electricity comes from fossil fuels like coal or natural gas, the carbon footprint is higher. Conversely, if the electricity comes from renewable sources like wind or solar, the carbon footprint is lower. According to Digiconomist, the Bitcoin network’s annual carbon footprint is estimated to be around 58.10 Mt CO2, which is comparable to the carbon emissions of countries like Greece or Chile.
E-Waste
Bitcoin mining requires specialized hardware known as ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits). These devices have a limited lifespan and can become obsolete as newer, more efficient models are developed. This can lead to the generation of e-waste, as old mining equipment is discarded. According to Digiconomist, the Bitcoin network’s annual e-waste generation is estimated to be around 11.5 kt, which is comparable to the e-waste generation of countries like Luxembourg or Malta.
Resource Depletion
The production of ASICs requires raw materials like metals and minerals. The extraction and processing of these resources can have environmental impacts, including habitat destruction, soil and water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Mitigation Efforts
Some Bitcoin miners are taking steps to mitigate their environmental impact. For example, some miners are using renewable energy sources like hydropower, wind, or solar to power their operations. Others are participating in carbon offset programs to compensate for their carbon emissions. Additionally, some miners are repurposing old mining equipment for other uses or recycling it to reduce e-waste.
Future of Bitcoin Mining

Bitcoin mining has evolved significantly since its inception in 2009. As the Bitcoin network grows and technology advances, the future of Bitcoin mining is likely to be shaped by several factors:
Halving Events
Every four years, the Bitcoin block reward is halved, reducing the number of new bitcoins created and earned by miners. The most recent halving occurred in May 2020, reducing the block reward from 12.5 to 6.25 bitcoins. The next halving is expected in 2024. As the block reward decreases, miners will rely more on transaction fees to maintain profitability. This could lead to increased competition among miners and higher transaction fees.
Increasing Difficulty
The difficulty of Bitcoin mining adjusts approximately every two weeks to ensure that blocks are added to the blockchain approximately every ten minutes. As more miners join the network and technology improves, the difficulty is likely to increase, making it harder to mine blocks. This could lead to further centralization of mining, as only large-scale operations with access to cheap electricity and advanced hardware can compete.
Environmental Concerns
The environmental impact of Bitcoin mining has become a topic of concern. The high energy consumption and carbon footprint of mining operations have led to calls for more sustainable practices. In the future, miners may be incentivized or regulated to use renewable energy sources, reduce their carbon emissions, and minimize e-waste. Some countries may also impose restrictions or taxes on Bitcoin mining to address environmental concerns.
Technological Advancements
The future of Bitcoin mining will be influenced by technological advancements. ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) have become the standard for Bitcoin mining, but newer, more efficient models are continually being developed. Innovations in cooling systems, power management, and chip design could further improve mining efficiency and reduce costs.
Regulatory Changes
The regulatory environment for Bitcoin mining varies by country and is subject to change. Some countries have embraced Bitcoin mining, while others have imposed restrictions or bans. Regulatory changes could affect the location and operations of mining farms, as well as the profitability of mining. Miners may seek out jurisdictions with favorable regulations, low electricity costs, and a stable political climate.
Decentralization Efforts
The centralization of Bitcoin mining in a few large pools has raised concerns about the security and decentralization of the network. In the future, efforts may be made to decentralize mining and reduce the influence of large pools. This could involve changes to the mining algorithm, the development of decentralized mining pools, or the promotion of small-scale mining.
Conclusion
Bitcoin mining is a complex and resource-intensive process that plays a crucial role in the security and decentralization of the Bitcoin network. It involves solving cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. Miners are rewarded with newly minted Bitcoins and transaction fees for their efforts.
Over the years, Bitcoin mining has evolved from a hobbyist activity to a highly competitive industry. The increasing difficulty of mining and the decreasing block rewards have made it challenging for individual miners to compete. As a result, mining pools have become the dominant force in the Bitcoin mining landscape, allowing miners to combine their computational power and share the rewards.
The environmental impact of Bitcoin mining has become a topic of concern. The high energy consumption and carbon footprint of mining operations have led to calls for more sustainable practices. Some miners are using renewable energy sources and participating in carbon offset programs to mitigate their environmental impact. However, more needs to be done to make Bitcoin mining more sustainable.
The future of Bitcoin mining will be shaped by factors such as halving events, increasing difficulty, environmental concerns, technological advancements, regulatory changes, and decentralization efforts. As the Bitcoin network matures and the industry evolves, miners will need to adapt to changing conditions and explore new strategies to remain competitive and profitable.
Bitcoin mining is a fascinating and dynamic field that offers insights into the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. It is a testament to the power of decentralized networks and the potential of digital currencies to revolutionize the financial system. As Bitcoin continues to grow in popularity and adoption, the role of miners in securing and maintaining the network will become even more critical.
FAQs
What is Bitcoin mining for dummies?
Bitcoin mining is the process of solving complex mathematical puzzles using computer hardware to confirm transactions on the Bitcoin network. Miners are rewarded with newly minted Bitcoins for their work. It’s like a competition where the fastest computer wins the most money.
How to withdraw Bitcoin from mining base?
To withdraw Bitcoin from a mining base, you need to have a Bitcoin wallet. Once you have a wallet, you can provide your wallet address to the mining base or pool where you are mining. They will send your earned Bitcoin to your wallet, and you can then use it as you wish.
How much can you make a month mining Bitcoin?
The amount you can make mining Bitcoin varies depending on factors like the current price of Bitcoin, the total computing power of the network, the amount of electricity you use, and the cost of electricity in your area. It can range from a few dollars to thousands of dollars per month.
How much does a Bitcoin mining rig cost?
A Bitcoin mining rig, specifically an ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) miner, can cost anywhere from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars. The price depends on factors like the miner’s hash rate, efficiency, and brand. As of 2024, a high-end ASIC miner like the Antminer S19 Pro can cost around $12,000 to $15,000.
How to start Bitcoin mining on phone?
There is no practical way to mine Bitcoin on a phone. Bitcoin mining requires significant computational power, and modern smartphones are not powerful enough to mine Bitcoin profitably.
How to start Bitcoin mining for free?
There is no way to start Bitcoin mining for free. Bitcoin mining requires investment in hardware and electricity. While there are some cloud mining services that offer free trials, they are usually not profitable and may have hidden fees or risks.
When will Bitcoin mining end?
Bitcoin mining will end when the maximum supply of 21 million Bitcoins has been reached. This is expected to happen around the year 2140. After that, miners will no longer receive block rewards, but they will still earn transaction fees for confirming transactions on the network.


