What is Bitcoin? This question has echoed around the globe as Bitcoin continues to shape the digital economy. Bitcoin, the first-ever cryptocurrency, has revolutionized the way we perceive and interact with money. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Bitcoin, its history, workings, and its potential future.
Table of Contents
History of Bitcoin
The Inception of Bitcoin
The story of Bitcoin begins in the midst of the 2008 global financial crisis. The traditional banking system was on the brink of collapse, and trust in financial institutions was at an all-time low. It was in this climate that the Bitcoin whitepaper, titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System,” was published by an individual or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. The whitepaper proposed a system for a decentralized digital currency, free from control by any government or financial institution.
The first block of the Bitcoin blockchain, known as the “genesis block” or “Block 0,” was mined by Nakamoto in January 2009. Embedded in the code of this block was a headline from The Times newspaper: “The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks.” This message is widely interpreted as a critique of the instability caused by fractional-reserve banking.
The Anonymous Creator: Satoshi Nakamoto

The identity of Satoshi Nakamoto remains one of the biggest mysteries in the world of cryptocurrency. Despite numerous theories and claimed ‘unmaskings’, the true identity or identities of Nakamoto remain unknown. Nakamoto was involved in the development of Bitcoin until mid-2010, after which they handed over control of the source code repository and network alert key to Gavin Andresen, a software developer involved in Bitcoin from its early days. Nakamoto also transferred several related domains to various prominent members of the Bitcoin community. After this, Nakamoto vanished from the public eye.
Key Milestones in Bitcoin’s History
Bitcoin’s history is marked by several key milestones. In May 2010, the first known commercial transaction using Bitcoin took place when programmer Laszlo Hanyecz bought two Papa John’s pizzas for 10,000 BTC. At the time, the transaction was roughly worth $41.
In February 2011, Bitcoin achieved parity with the US dollar, making one BTC equal to one USD. This was a significant milestone that helped to increase Bitcoin’s visibility in the mainstream financial world.
In 2013, Bitcoin’s price first exceeded $1,000, a dramatic increase from its initial value. However, this was followed by a significant price drop, demonstrating the high volatility that Bitcoin would become known for.
In 2017, Bitcoin reached its then all-time high of nearly $20,000, drawing widespread media attention. However, this was followed by a ‘crypto winter,’ a period of declining prices throughout 2018.
In 2020, Bitcoin broke its previous record, reaching a new all-time high. This bull run continued into 2021, with Bitcoin’s price exceeding $60,000.
In 2021, Bitcoin reached a new all-time high of $61,699 on March 13, 2021.
Throughout its history, Bitcoin has faced numerous challenges, including regulatory scrutiny, security issues, and internal disagreements within the community. Despite these challenges, Bitcoin has survived and grown, proving its resilience and potential as a disruptive technology.
Understanding Cryptocurrency
So, what is cryptocurrency? Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual form of currency that uses cryptography for security. It operates independently of a central bank.
Cryptocurrencies work using a technology called blockchain. Blockchain is a decentralized technology spread across many computers that manage and record transactions.
The Role of Blockchain Technology in Cryptocurrency
Blockchain technology is the backbone of cryptocurrency, and it’s what makes it possible for digital currencies like Bitcoin to operate in a decentralized, secure, and transparent manner.
Decentralization
One of the key features of blockchain technology is its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional financial systems, where transactions are processed and verified by a central authority (like a bank or government), blockchain operates on a network of computers (nodes) distributed around the world. Each node has a copy of the entire blockchain, and they work together to validate and record transactions. This decentralization means that no single entity has control over the entire network, making it resistant to censorship and manipulation.
Security
Blockchain technology also provides a high level of security. Each block in the blockchain contains a list of transactions, and these blocks are linked to each other in a chain through a process called hashing. Each block contains a unique code (hash) and the hash of the previous block in the chain. This means that if someone tries to alter a transaction in a block, the hash of that block will change, breaking the link with the next block in the chain and alerting the network to the tampering. This makes blockchain incredibly secure against fraud and hacking.
Transparency
Blockchain’s transparency is another crucial feature. Since every transaction on the blockchain is recorded and visible to all nodes in the network, it’s nearly impossible to make fraudulent transactions without being detected. This transparency also allows for easy verification of transactions and balances, which is essential in the world of digital currencies.
How Bitcoin Works

Bitcoin operates on principles that are fundamentally different from traditional currencies. Here’s a deeper look into how it works:
Explanation of Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining is the process by which new bitcoins are entered into circulation. It also serves to secure the network and process all Bitcoin transactions. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems that validate each transaction and add it to the blockchain. The first miner to solve the problem gets to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain and is rewarded with a certain number of new bitcoins (currently 6.25, but this amount halves approximately every four years in an event known as “halving“).
Understanding Bitcoin Transactions
When a Bitcoin transaction is made, it needs to be confirmed before it can be completed. Bitcoin miners confirm the transactions by including them in the blocks they mine. Once a block is added to the blockchain, the transaction is considered confirmed. This process usually takes about 10 minutes for Bitcoin, but it can vary depending on the network’s congestion and transaction fees.
Each Bitcoin transaction is recorded on the blockchain with the sender’s and recipient’s public keys (Bitcoin addresses) and the amount of coins transferred. The transaction also needs to be signed off by the sender with their private key. All of this is done without any central authority or bank.
The Role of Bitcoin Wallets
Bitcoin wallets are essential for managing and securing your bitcoins. A Bitcoin wallet can be a device, program, or service which allows you to store your Bitcoin, make transactions, and check your balance. There are different types of Bitcoin wallets, including desktop, mobile, web, and hardware wallets.
Each Bitcoin wallet has a private key and a public key. The public key, also known as the Bitcoin address, is what you share with others to receive Bitcoin. The private key is a secret code associated with the Bitcoin address. It’s used to sign transactions, providing mathematical proof that they have come from the owner of the wallet.
Here’s a chart of some of the most famous Bitcoin wallets:
| Wallet Name | Type | Security Level | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ledger Nano X | Hardware | High | Ledger Nano X |
| TREZOR T | Hardware | High | TREZOR T |
| Ledger Nano S | Hardware | High | Ledger Nano S |
| Coinbase Wallet | Online/Hot Wallet | Medium | Coinbase Wallet |
| Electrum | Software/Desktop | Medium | Electrum |
Please note that the security level is subjective and depends on how you handle and secure your wallet. Hardware wallets are generally considered the most secure, but they require more effort to use. Online and software wallets are more convenient but have a higher risk because they are connected to the internet.
Bitcoin Blockchain and Its Importance
The Bitcoin blockchain is a public ledger that records all Bitcoin transactions. It’s maintained by a network of nodes (computers running the Bitcoin software), and anyone can access it and verify the transactions.
The blockchain ensures that the same bitcoins can’t be spent twice, which was a major problem for digital currencies before Bitcoin. It does this by recording every transaction in a block and adding it to a chain of blocks. Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it can’t be changed, making Bitcoin transactions immutable.
The Value of Bitcoin
The value of Bitcoin, like any other commodity or currency, is determined by a variety of factors. Here’s a deeper look into what influences Bitcoin’s value:
Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Value
Several factors can influence the value of Bitcoin:
Supply and Demand
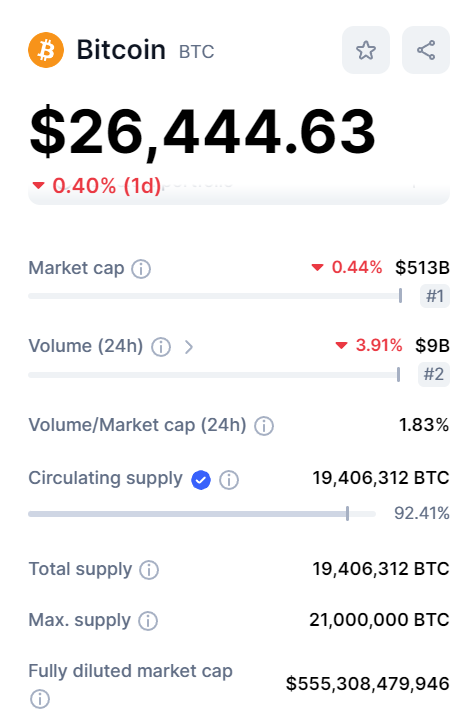
Supply and demand is a fundamental concept in economics that influences the price of goods and services in a market, including cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
- Supply: The supply of Bitcoin is determined by the Bitcoin protocol, which was designed by Satoshi Nakamoto. The protocol established that only 21 million Bitcoins will ever be created, a number that cannot be changed. New Bitcoins are introduced into the market through a process called mining, where miners solve complex mathematical problems to add new blocks to the Bitcoin blockchain. The rate at which new Bitcoins are created is halved approximately every four years in an event known as “halving”. This means that the supply of new Bitcoins decreases over time, which can lead to an increase in price if demand remains strong.
- Demand: The demand for Bitcoin is influenced by a variety of factors, including public sentiment, market speculation, and regulatory news. As more people learn about Bitcoin and become interested in owning it, the demand for Bitcoin increases. If the demand for Bitcoin exceeds the supply, the price will rise. Conversely, if the supply of Bitcoin exceeds demand, the price will fall.
In the case of Bitcoin, its capped supply and decreasing rate of new Bitcoin creation, combined with increasing demand, has contributed to its significant price increases over time. However, it’s important to note that while supply is predictable due to the Bitcoin protocol, demand can be highly volatile and influenced by many unpredictable factors, leading to the price volatility that Bitcoin is known for.
Market Sentiment
Market sentiment, also known as investor sentiment, is the overall attitude of investors toward a particular financial market or specific asset. It represents the general perceived attitude of investors as to anticipated price development in a market. In the context of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, market sentiment can significantly impact the value and price volatility of these digital assets.
Here are some ways market sentiment can influence Bitcoin:
- Positive Sentiment: Positive market sentiment can occur when there’s favorable news about Bitcoin, such as technological advancements, positive regulatory news, or increased adoption by individuals and businesses. For example, when a major company like Tesla announces that it has invested in Bitcoin or will accept it as payment, it can lead to increased confidence and excitement among investors, driving up demand and price.
- Negative Sentiment: Conversely, negative market sentiment can be triggered by unfavorable news, such as regulatory crackdowns, security breaches, or negative comments from influential individuals or institutions. This can lead to fear, uncertainty, and doubt (often referred to as “FUD” in the crypto community), causing investors to sell off their holdings, which can drive down the price.
- Market Trends and Momentum: Market sentiment is also influenced by price trends and momentum. When Bitcoin’s price is on an upward trend, it can lead to bullish sentiment, where investors believe the price will continue to rise. This can become a self-fulfilling prophecy, as more investors buy in, further driving up the price. The opposite is true when the price is on a downward trend, leading to bearish sentiment.
- Social Media and News Coverage: In today’s digital age, social media and news coverage play a significant role in shaping market sentiment. Positive or negative news stories, trending hashtags, or viral social media posts can significantly sway investor sentiment in a short period.
In summary, market sentiment is a crucial factor in the price of Bitcoin. It’s influenced by a variety of factors, both tangible (like regulatory news) and intangible (like investor emotions). Understanding market sentiment can help investors make informed decisions, but it’s also important to remember that sentiment can change quickly and is just one of many factors to consider when investing in Bitcoin.
Regulatory News

Regulatory news refers to the announcements, decisions, or actions taken by government bodies or regulatory authorities that pertain to the rules and regulations surrounding a particular sector or activity. In the context of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, regulatory news can significantly impact the value, operations, and perception of these digital assets.
Here are some ways regulatory news can influence Bitcoin:
- Legal Status and Recognition: When a country officially recognizes Bitcoin as a legal form of payment or as a commodity, it can lead to increased adoption and a rise in Bitcoin’s value. For example, in 2020, the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) in the United States allowed national banks to provide custody services for cryptocurrencies, which was seen as a significant step towards mainstream acceptance.
- Regulatory Restrictions or Bans: Conversely, if a country imposes restrictions or outright bans on Bitcoin, it can lead to a decrease in its value. For instance, when China announced a crackdown on Bitcoin mining and trading in 2021, it led to a significant drop in Bitcoin’s price.
- Taxation Policies: The way Bitcoin is taxed can also influence its value. If a country imposes high taxes on Bitcoin profits, it could discourage investors and affect the price negatively. On the other hand, favorable tax policies could encourage investment and drive up the price.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) Regulations: Governments worldwide are implementing AML and KYC regulations for cryptocurrencies to prevent illegal activities like money laundering and fraud. While these regulations can limit the anonymity that some users seek in Bitcoin, they can also lead to greater trust and stability in the market.
- Securities Regulations: If a regulatory body, like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), decides to classify Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies as securities, it could have significant implications for how these assets are traded and regulated.
Regulatory news can have a significant impact on Bitcoin’s value, adoption, and perception in the market. It’s crucial for investors and users to stay informed about the regulatory landscape to navigate the Bitcoin market effectively.
Technological Changes
Technological advancements and changes to the Bitcoin protocol can impact Bitcoin’s value. For instance, updates that improve the scalability, security, or efficiency of the Bitcoin network can make Bitcoin more attractive to users and investors, potentially driving up the price.
Bitcoin Dominance
Bitcoin dominance refers to the percentage of the total cryptocurrency market capitalization that Bitcoin occupies. It’s a measure of Bitcoin’s value relative to the value of all other cryptocurrencies combined. High Bitcoin dominance indicates that Bitcoin holds a majority share of the cryptocurrency market, reflecting its status as the first and most widely adopted cryptocurrency. Conversely, low Bitcoin dominance suggests a greater market preference for altcoins (all cryptocurrencies other than Bitcoin). Bitcoin dominance can influence the market dynamics of other cryptocurrencies, as periods of high Bitcoin dominance are often associated with less capital flowing into altcoins, and vice versa.
Historical Price Trends of Bitcoin
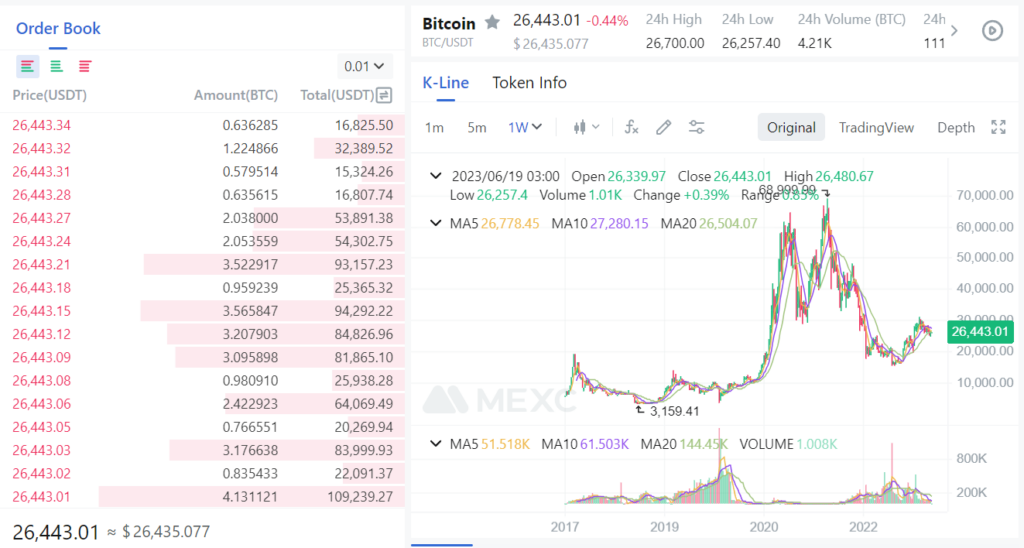
Bitcoin’s price has seen significant volatility since its inception. It started with no value when it was first created in 2009. The first known price of Bitcoin was in 2010 when it was valued at less than a penny. Since then, it has experienced several boom and bust crypto market cycles, reaching an all-time high of over $60,000 in 2021.
Bitcoin’s Volatility and Its Implications
Bitcoin’s volatility refers to the rate at which the price of Bitcoin increases or decreases for a set of returns. Bitcoin’s price is known for wild price swings, which can result in significant price changes over a short period. This volatility can present opportunities for traders, but it can also pose significant risks. It’s important for investors to consider their risk tolerance and investment goals when dealing with Bitcoin.
Investing in Bitcoin

Investing in Bitcoin has become increasingly popular over the past decade as more people have come to understand the potential benefits and risks associated with this digital asset. Here’s a detailed look at what investing in Bitcoin entails:
Pros and Cons of Investing in Bitcoin
| Pros of Investing in Bitcoin | Cons of Investing in Bitcoin |
|---|---|
| Potential for High Returns: Bitcoin has shown significant growth since its inception. | Volatility: Bitcoin prices can fluctuate wildly in short periods. |
| Liquidity: Bitcoin is traded on various exchanges, making it easy to buy and sell. | Regulatory Uncertainty: The legal status of Bitcoin varies by country and can change. |
| Accessibility: Bitcoin can be bought in fractions, allowing for low entry levels. | Lack of Consumer Protections: If your Bitcoin is stolen, there’s no guaranteed way to get it back. |
Pros:
- Potential for High Returns: Bitcoin has shown significant growth since its inception, and some investors have seen substantial returns.
- Liquidity: Bitcoin is traded on various exchanges, making it relatively easy to buy and sell at any time.
- Accessibility: Bitcoin can be bought in fractions, allowing for low entry levels. You don’t need to buy a whole Bitcoin; you can start with just a small fraction.
Cons:
- Volatility: Bitcoin prices can fluctuate wildly in short periods, leading to potential losses.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The legal status of Bitcoin varies by country and can change, potentially impacting its value.
- Lack of Consumer Protections: If your Bitcoin is stolen, there’s no guaranteed way to get it back.
How to Buy Bitcoin
Bitcoin can be purchased on a cryptocurrency exchange using traditional currency or other cryptocurrencies. Some popular exchanges include Mexc.com, Coinex.com, and Gate.io. You’ll need to create an account, go through a verification process, deposit funds, and then you can exchange those funds for Bitcoin.
Tips for Investing in Bitcoin Safely
- Diversify: Don’t put all your investment in Bitcoin. Diversify your portfolio to mitigate risk.
- Research: Stay updated with Bitcoin news. Understanding market trends can help you make informed decisions.
- Secure Your Investment: Use a secure wallet to store your Bitcoin. Consider using hardware wallets for large amounts.
- Don’t Invest More Than You Can Afford to Lose: Due to its volatility, you should only invest money that you can afford to lose in Bitcoin.
Remember, investing in Bitcoin, like any investment, involves risk. It’s important to do thorough research and consider seeking advice from a financial advisor.
Bitcoin and the Law

The legal status and regulatory environment for Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies vary significantly around the world. Here’s a deeper look into how Bitcoin interacts with the law:
Legal Status of Bitcoin Around the World
The legal status of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies varies greatly from country to country and is still undefined or changing in many of them. While some countries have explicitly allowed their use and trade, others have banned or restricted it.
For instance, in the European Union, Bitcoin is legal and VAT/GST is not applicable to the conversion between traditional (fiat) currency and Bitcoin. However, VAT/GST and other taxes still apply to transactions made using Bitcoin for goods and services.
In the United States, Bitcoin is considered a convertible decentralized virtual currency and is taxed as property. Financial institutions dealing with Bitcoin are required to register with the U.S. FinCEN as a money services business, design and enforce an anti-money laundering (AML) program, and keep appropriate records and make reports to FinCEN.
In contrast, countries like Algeria, Egypt, and Morocco have declared Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies illegal. In Nigeria, while Bitcoin is legal, a banking ban has been imposed on Bitcoin transactions.
In Asia, the legal status of Bitcoin varies widely. For instance, in India, Bitcoin is neither prohibited nor allowed, and the Supreme Court of India lifted the ban on cryptocurrency imposed by the Reserve Bank of India in 2020. On the other hand, in countries like Afghanistan, Bitcoin trading is banned.
Please note that this information is subject to change as countries continue to develop and adapt their regulations around Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. Always consult with a legal expert or conduct thorough research to understand the current legal status of Bitcoin in a specific country.
Bitcoin and Tax Implications
In many jurisdictions, Bitcoin is subject to capital gains tax. This means that if you buy Bitcoin and sell it at a higher price, you may be required to pay tax on the profit. The exact rules and rates can vary greatly, so it’s important to consult with a tax professional or do thorough research to understand the tax implications in your specific location.
Bitcoin and Anti-Money Laundering Laws
Due to the pseudonymous nature of Bitcoin transactions, there have been concerns about its potential use in illegal activities, such as money laundering or financing of terrorism. As a result, many countries have implemented anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) regulations for Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. These regulations often involve Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures, where cryptocurrency exchanges are required to verify the identity of their customers.
In summary, the legal and regulatory environment for Bitcoin is complex and rapidly evolving. It’s crucial for users and investors to stay informed about the laws and regulations in their specific location. It’s also important to remember that while Bitcoin offers many opportunities, it also comes with certain legal responsibilities.
Future of Bitcoin
The future of Bitcoin, like any other cryptocurrency, is subject to a great deal of speculation. However, there are several key trends and factors that could shape its trajectory.
Predicted Trends for Bitcoin
- Mainstream Adoption: Bitcoin is expected to continue its journey towards mainstream adoption. This is likely to be driven by growing acceptance of Bitcoin as a form of payment by businesses and merchants, increased use of Bitcoin in remittances, especially in developing countries, and the potential for Bitcoin to serve as a hedge against inflation.
- Technological Advancements: Technological advancements could also shape the future of Bitcoin. For instance, the development of the Lightning Network could make Bitcoin transactions faster and cheaper, thereby making it more usable for everyday transactions.
- Regulatory Developments: The future of Bitcoin will also be influenced by regulatory developments. While some countries have embraced Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, others have banned or restricted their use. The introduction of new regulations or changes to existing ones could significantly impact Bitcoin’s future.
Potential Challenges for Bitcoin
- Scalability Issues: One of the major challenges for Bitcoin is its scalability issue. The Bitcoin network can only process a limited number of transactions per second, which can lead to delays and higher transaction fees.
- Environmental Concerns: Bitcoin mining consumes a significant amount of energy, leading to concerns about its environmental impact. This could lead to regulatory backlash or a shift in public sentiment against Bitcoin.
- Regulatory Risks: As mentioned earlier, regulatory risks are a significant concern for Bitcoin. If major economies impose strict regulations or outright bans on Bitcoin, it could severely impact its value and adoption.
Bitcoin’s Potential Impact on Global Finance
- Decentralization of Finance: Bitcoin, as a decentralized currency, has the potential to disrupt traditional financial systems by eliminating the need for intermediaries like banks and financial institutions.
- Inflation Hedge: With its capped supply, Bitcoin could serve as a hedge against inflation, particularly in countries with unstable currencies.
- Financial Inclusion: Bitcoin could also contribute to financial inclusion by providing access to financial services to the unbanked population.
While the future of Bitcoin holds much promise, it is also fraught with challenges. Its trajectory will be determined by a combination of technological advancements, regulatory developments, and changes in the global financial landscape.
Conclusion
Bitcoin, the first and most prominent cryptocurrency, has revolutionized the concept of currency and financial transactions. It has introduced the world to the benefits of decentralization, blockchain technology, and digital currencies.
From its inception by the anonymous Satoshi Nakamoto to its current status as a highly volatile but potentially lucrative investment, Bitcoin has come a long way. Its journey has been marked by rapid growth, intense speculation, and significant regulatory scrutiny.
The technology behind Bitcoin, blockchain, has proven to be a groundbreaking innovation with applications beyond just cryptocurrencies. It has the potential to transform various sectors, including finance, supply chain management, and healthcare, among others.
Investing in Bitcoin, like any other investment, comes with its own set of risks and rewards. While it has the potential for high returns, it is also subject to high volatility and regulatory uncertainty. Therefore, potential investors should conduct thorough research and consider their risk tolerance before investing in Bitcoin.
The legal status of Bitcoin varies significantly around the world, with some countries embracing it, others imposing restrictions, and some banning it outright. This regulatory landscape is continually evolving and can significantly impact Bitcoin’s value and adoption.
As for the future of Bitcoin, it holds much promise but is also fraught with challenges. Its trajectory will be determined by a combination of technological advancements, regulatory developments, and changes in the global financial landscape.
Bitcoin is a complex and fascinating digital asset that has had a significant impact on our understanding of currency, finance, and the potential of blockchain technology. As we move forward, Bitcoin is likely to continue playing a significant role in the global financial ecosystem.
FAQs
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency, without a central bank or single administrator, that can be sent from user to user on the peer-to-peer bitcoin network without the need for intermediaries.
Who created Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was created by an unknown person or group of people using the name Satoshi Nakamoto. The identity of Satoshi Nakamoto is still a mystery.
How does Bitcoin work?
Bitcoin works by recording every transaction that takes place on its network in a public ledger called the blockchain. New transactions are added in blocks and each block is added to the blockchain by Bitcoin miners.
Is Bitcoin legal?
The legality of Bitcoin depends on where you’re located. In some countries, Bitcoin is legal and regulated, while in others it’s banned or restricted.
How can I buy Bitcoin?
Bitcoin can be purchased on a cryptocurrency exchange using traditional currency or other cryptocurrencies. Some popular exchanges include Mexc, Coinex, Gate.io
Is Bitcoin a good investment?
Whether Bitcoin is a good investment depends on your individual circumstances, risk tolerance, and investment goals. While Bitcoin has the potential for high returns, it’s also highly volatile and can be risky.
What determines the price of Bitcoin?
The price of Bitcoin is determined by supply and demand. Factors such as public sentiment, regulatory news, and changes in economic environments can also affect the price.
Can Bitcoin be converted to cash?
Yes, Bitcoin can be converted to cash through a cryptocurrency exchange or a Bitcoin ATM.


