Cryptocurrency has taken the world by storm, offering a decentralized way to conduct transactions and invest. One of the pillars of this digital revolution is cryptocurrency mining. If you’ve ever wondered how to mine cryptocurrency and what it takes to get started, you’re in the right place. This article aims to be your ultimate guide, covering everything from the types of mining to the hardware and software you’ll need.
Table of Contents
What is Cryptocurrency Mining?
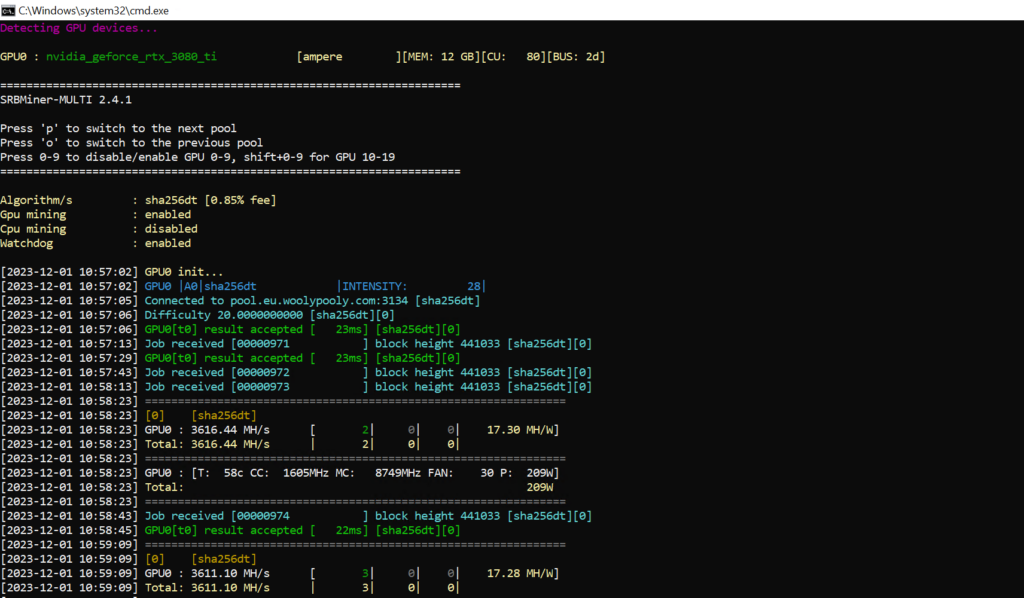
Cryptocurrency mining is a complex computational process that serves multiple purposes in the world of digital currencies. At its core, mining involves solving intricate mathematical problems, known as cryptographic hash functions, to validate transactions and secure them onto a blockchain. But what does this mean, and why is it so vital? Let’s delve deeper.
Definition
Cryptocurrency mining is the act of participating in a blockchain network to validate transactions. Miners use specialized hardware to solve complex algorithms, and in return, they are rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrency tokens. This process is essential for the functioning and security of a blockchain network.
The Mining Process
When a transaction is initiated, it goes into a pool of unconfirmed transactions. Miners pick transactions from this pool and attempt to confirm them by solving a mathematical problem. This problem is unique to each block of transactions and requires a significant amount of computational power to solve. Once the problem is solved, the block of transactions is added to the blockchain, and the miner is rewarded with a certain number of newly created cryptocurrency tokens.
Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake
Most cryptocurrencies use either a Proof of Work (PoW) or a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm to validate transactions. In PoW, miners compete to solve complex problems, and the first one to solve it gets the reward. In PoS, validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. While PoW is more common and well-known due to Bitcoin, PoS is gaining popularity for its energy efficiency.
Role in Network Security
Mining does more than just validate transactions; it also plays a crucial role in maintaining the security of a blockchain network. By solving complex problems, miners make it computationally unfeasible for malicious actors to alter past transactions. This ensures the integrity and chronological order of the blockchain, making it secure and trustworthy.
Types of Cryptocurrency Mining
Cryptocurrency mining can be done in several ways (depends on crypto you want to mine), each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these methods can help you make an informed decision on how to proceed with your mining venture.
CPU Mining
Pros
- Low Entry Cost: CPU mining is the most basic form of mining and doesn’t require specialized equipment.
- Ease of Use: Almost any computer can be used for CPU mining.
Cons
- Low Efficiency: CPU mining is generally less efficient and slower compared to other methods.
- High Energy Consumption: Despite its low efficiency, it can still consume a lot of electricity.
GPU Mining
Pros
- Higher Efficiency: GPUs are more powerful than CPUs and can solve cryptographic puzzles faster.
- Versatility: Suitable for mining various types of cryptocurrencies.
Cons
- Higher Initial Cost: A good GPU can be expensive.
- Energy Consumption: While more efficient than CPU mining, GPUs still consume a significant amount of electricity.
ASIC Mining
Pros
- High Efficiency: ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) are designed for specific cryptographic algorithms, making them highly efficient.
- Low Energy Consumption: Due to their efficiency, they consume less electricity per hash.
Cons
- High Initial Cost: ASIC miners can be quite expensive to purchase.
- Lack of Versatility: ASICs are tailored for specific cryptocurrencies, making them less versatile than GPUs.
Cloud Mining
Pros
- No Hardware Required: You rent mining power from a data center.
- Ease of Use: No need to worry about setup, maintenance, or electricity costs.
Cons
- Risk of Scams: Always research thoroughly as there are many fraudulent cloud mining services.
- Less Profit: You have to share a portion of your earnings with the cloud mining service.
FPGA Mining (Field-Programmable Gate Array)
Pros
- Efficiency: FPGAs offer a good balance between the efficiency of ASICs and the versatility of GPUs.
- Customization: They can be reprogrammed to mine different algorithms, offering some level of versatility.
Cons
- Moderate Initial Cost: While cheaper than a high-end ASIC, FPGAs can still be costly.
- Technical Complexity: Requires some technical knowledge to reprogram for different algorithms.
HDD Mining (e.g., Chia Coin)
HDD mining, also known as “storage mining,” utilizes hard disk drives to validate transactions and secure the network. This type of mining is less energy-intensive compared to traditional methods and is exemplified by cryptocurrencies like Chia Coin.
Pros
- Energy-efficient
- Lower hardware costs
- Less heat generation
Cons
- Limited to specific cryptocurrencies
- Lower profitability compared to GPU/ASIC mining
- Requires large storage capacity
Arduino Mining (e.g., Duino Coin)
Arduino mining is a low-cost, entry-level approach to mining that uses Arduino microcontrollers. This type of mining is suitable for beginners and those who want to mine on a smaller scale. Duino Coin is one of the cryptocurrencies that can be mined using Arduino.
Pros
- Low entry cost
- Educational and beginner-friendly
- Low energy consumption
Cons
- Limited scalability
- Lower profitability
- Limited to specific cryptocurrencies
| Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | Low entry cost, Ease of use | Low efficiency, High energy |
| GPU | Higher efficiency, Versatility | Higher cost, Energy consumption |
| ASIC | High efficiency, Low energy | High cost, Lack of versatility |
| Cloud | No hardware, Ease of use | Risk of scams, Less profit |
| FPGA | Efficiency, Customization | Moderate cost, Technical complexity |
| HDD | Energy-efficient, Low cost | Limited cryptocurrencies, Lower profit |
| Arduino | Low cost, Beginner-friendly | Limited scalability, Lower profit |
Hardware Requirements
Choosing the right hardware is a critical step in how to mine cryptocurrency. The type of hardware you’ll need depends on the type of mining you plan to do. Below are the hardware requirements for each type of mining:
CPU Mining
Basic Requirements
- Processor: A multi-core processor for better performance.
- RAM: At least 8GB for smooth operation.
- Storage: A minimum of 50GB free space on your hard drive.
Recommendations
- Processor: AMD Ryzen7 or higher.
- RAM: 16GB or higher for better performance.
GPU Mining
Basic Requirements
- Graphics Card: A high-end graphics card with at least 4GB of RAM.
- Power Supply: A power supply unit (PSU) with enough wattage to support your graphics cards.
- Cooling System: Adequate cooling to prevent overheating.
Recommendations
- Graphics Card: NVIDIA GeForce RTX4090.
- Power Supply: At least a 750W PSU.
- Cooling System: High-quality fans or a liquid cooling system.
ASIC Mining
Basic Requirements
- ASIC Miner: A specialized ASIC mining rig.
- Power Supply: A compatible power supply unit.
- Cooling System: Adequate cooling to prevent overheating.
Recommendations
- ASIC Miner: Antminer KS3 for Kaspa mining.
- Power Supply: A PSU with at least 1600W.
- Cooling System: Industrial-grade cooling fans.
Cloud Mining
- No hardware required: Since you’re renting computing power, you don’t need any hardware.
FPGA Mining
Basic Requirements
- FPGA Board: A board with a suitable FPGA chip.
- Power Supply: A compatible power supply unit.
- Cooling System: Adequate cooling to prevent overheating.
Recommendations
- FPGA Board: Xilinx Varium C1100 or Intel Arria 10 GX.
- Power Supply: At least a 600W PSU.
- Cooling System: High-quality fans or a liquid cooling system.
HDD Mining
Basic Requirements
- HDD Capacity: The larger the hard disk capacity, the more coins you can mine.
- Motherboard: An integrated motherboard or a GPU with a built-in CPU is generally sufficient.
Recommendations
- HDD Capacity: A minimum of 2TB is recommended for effective mining.
- External Hard Drive Box: For expanding capacity.
Arduino Mining
Basic Requirements
- Arduino Board: Any compatible Arduino board will suffice.
- USB Cable: To connect the Arduino board to your computer.
Recommendations
- Arduino Uno or Mega: These boards offer better performance and more GPIO pins for scalability.
- Quality USB Cable: To ensure a stable connection.
| Type | Basic Requirements | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | Multi-core processor, 4GB RAM, 50GB storage | AMD Ryzen9 3950X, 32GB RAM |
| GPU | High-end graphics card, PSU, Cooling system | RTX 4090, 750W PSU, Quality fans |
| ASIC | ASIC Miner, PSU, Cooling system | Antminer KS3 |
| Cloud | None | N/A |
| FPGA | FPGA Board, PSU, Cooling system | Xilinx Varium C1100, 600W PSU |
| HDD | HDD Capacity, Motherboard | 2TB HDD and more, External Hard Drive Box |
| Arduino | Arduino Board, USB Cable | Arduino Uno/Mega, Quality USB Cable |
Software Requirements
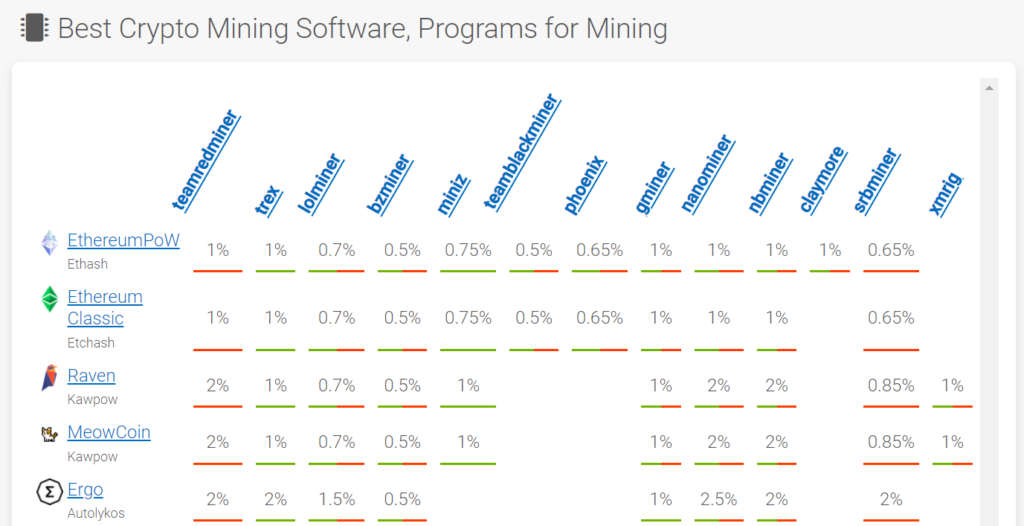
Choosing the right software is as crucial as selecting the appropriate hardware. The software you’ll need varies depending on the type of mining you plan to engage in. Below are the software requirements for each type of mining:
CPU Mining
Basic Requirements
- Mining Software: A software that supports CPU mining.
Recommendations
- XMRig: This is the best software for CPU mining. It supports a variety of algorithms and is user-friendly.
GPU Mining
Basic Requirements
- Mining Software: Software that is compatible with your GPU.
Recommendations
- lolMiner: Optimized for AMD GPUs and supports multiple algorithms.
- GMiner: Known for its stability and support for multiple algorithms.
- BZMiner: Offers high performance and is suitable for both Nvidia and AMD GPUs.
ASIC Mining
Basic Requirements
- Firmware: Your ASIC will come with pre-installed firmware.
Optional
- Custom ASIC Firmware: Some miners prefer custom firmware for better performance.
- ASIC Monitoring OS: Platforms like Hiveon ASIC Hub can help you monitor and manage your ASIC devices more efficiently.
Cloud Mining
- No software required: Since you’re renting computing power, you don’t need any software. However, you may need a wallet to receive your mined coins.
FPGA Mining
Basic Requirements
- Mining Software: Software that supports FPGA mining.
Recommendations
- Teamredminer: Starting in version v0.9.0 TeamRedMiner(TRM) supports to mine ethash on two FPGA products based on Xilinx FPGAs: the Xilinx Varium C1100 and the SQRL Forest Kitten 33.
- OpenCL: This is commonly used for FPGA mining and offers a range of customization options.
| Type | Basic Requirements | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | Mining Software | XMRig |
| GPU | Mining Software | lolMiner, GMiner, BZMiner |
| ASIC | Firmware, Monitoring Software | Custom Firmware, Hiveon ASIC Hub |
| Cloud | None | N/A |
| FPGA | Mining Software | Teamredminer, OpenCL |
Choosing the Right Mining Pool
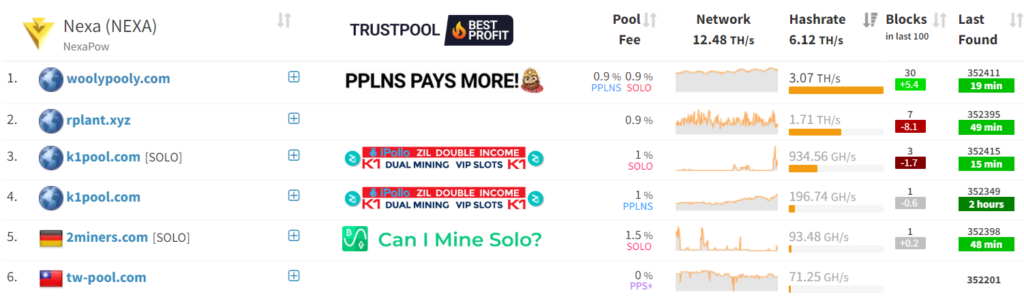
Mining on your own can be challenging and less profitable, especially for beginners. That’s why many miners opt to join a mining pool, where multiple participants combine their computational power to increase the chances of successfully mining a block and receiving rewards. However, not all mining pools are created equal. Here’s what you should consider when choosing the right mining pool:
Reputation
- Research: Always conduct thorough research to ensure the mining pool is reputable. Look for reviews, testimonials, and any red flags that could indicate a scam.
- Community: A strong, active community can often be a good indicator of a pool’s reliability and transparency.
Fees
- Structure: Some pools have a flat fee, while others take a percentage of your mining rewards.
- Hidden Fees: Be wary of pools that have low fees but make up for it with hidden charges.
Payout
- Frequency: Some pools offer daily payouts, while others may have weekly or even monthly payout schedules.
- Threshold: Check the minimum payout threshold to ensure it aligns with your mining goals.
Mining Algorithms Supported
- Compatibility: Make sure the pool supports the cryptocurrency and mining algorithm you intend to use.
- Variety: Some pools offer multiple algorithms, which can be beneficial if you plan to switch between different cryptocurrencies.
Geographic Location
- Server Locations: Choose a pool with servers close to your geographic location to reduce latency and improve mining efficiency.
- Regulations: Make sure the pool complies with the laws and regulations of its operating country.
User Interface and Features
- Dashboard: A user-friendly dashboard can make monitoring and controlling your mining activities easier.
- Advanced Features: Some pools offer features like hash rate monitoring, smartphone apps, and even mining optimization tips.
| Criteria | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Reputation | Research, Community |
| Fees | Structure, Hidden Fees |
| Payout | Frequency, Threshold |
| Algorithms Supported | Compatibility, Variety |
| Geographic Location | Server Locations, Regulations |
| UI and Features | Dashboard, Advanced Features |
Setting Up Your Mining Rig
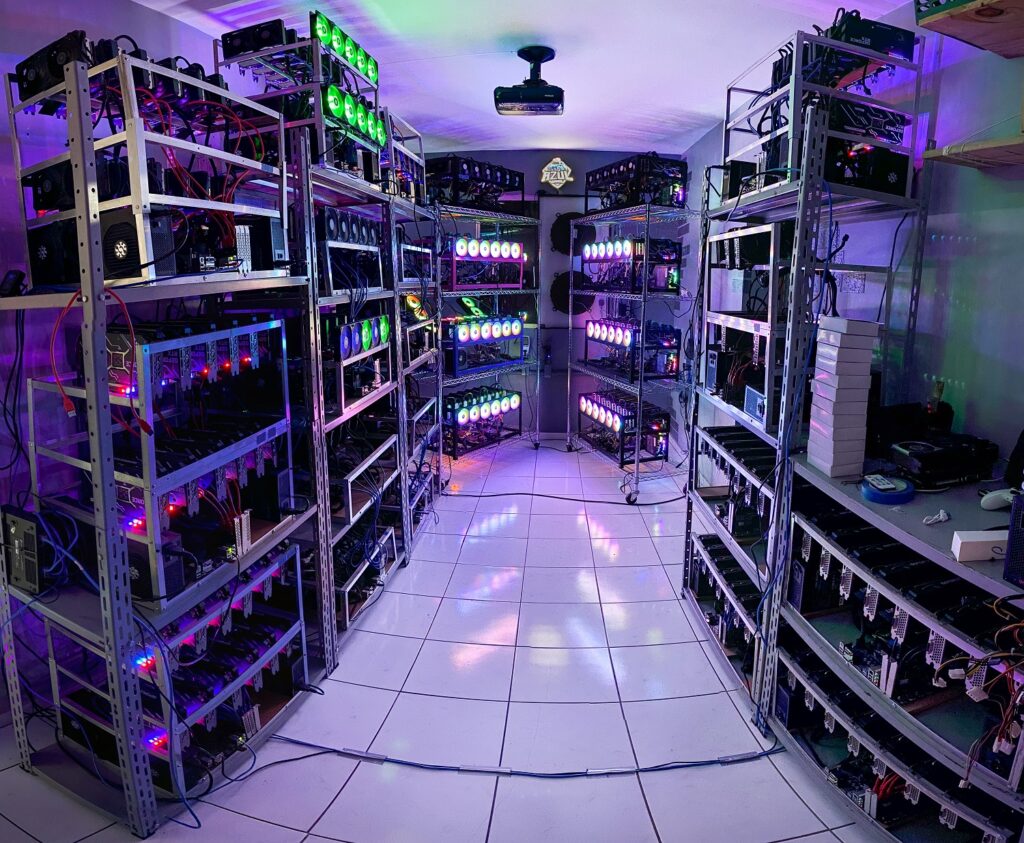


Setting up a mining rig might seem like a daunting task, but with the right guidance, it can be a straightforward and rewarding experience. Whether you’re using a CPU, GPU, ASIC, or FPGA, each type of hardware has its own set of requirements and steps for setup. Below is a comprehensive guide to help you set up your mining rig.
Preparing the Space
Before you even start assembling your hardware, you’ll need to prepare the space where your mining rig will operate. Consider the following:
- Ventilation: Ensure the space has good airflow to help with cooling.
- Electricity: Make sure you have enough electrical outlets for all your hardware.
- Safety: Keep the area free of clutter and flammable materials.
Assembling the Hardware
Once you’ve prepared your space, it’s time to assemble your hardware.
- CPU/GPU/FPGA: If you’re using one of these, you’ll likely need to assemble a PC-like structure. This involves installing the motherboard, processor, RAM, power supply, and your chosen mining hardware into a case.
- ASIC: These come pre-assembled. You’ll just need to connect them to a power source and your network.
Installing the Operating System
- Windows/Linux: If you’re using a CPU, GPU, or FPGA, you’ll need to install an operating system. Windows is more user-friendly but Linux is often considered more stable and secure for mining.
- ASIC: These usually come with a pre-installed operating system, so you can skip this step.
Installing Mining Software
Depending on your hardware, you’ll need to install the appropriate mining software.
- CPU: XMRig is highly recommended for CPU mining.
- GPU: lolMiner, GMiner, and BZMiner are popular choices.
- ASIC: No special software is needed, but you might optionally use custom ASIC firmware and monitoring systems like Hiveon ASIC Hub.
- FPGA: OpenCL is commonly used for FPGA mining.
Configuring and Testing
After installing the software, you’ll need to configure it.
- Settings: Each mining software will have its own set of configurations. This usually involves specifying which coin to mine, setting up your wallet address, and choosing a mining pool.
- Testing: Before fully committing, run the software to test if everything is working as expected. Monitor temperature levels, hash rates, and any errors that may occur.
Starting the Mining Process
Once everything is set up and tested, you can start the mining process.
- Launch: Open your mining software and start mining.
- Monitoring: Keep an eye on performance metrics and make adjustments as needed.
Mining Profitability

Mining can be a lucrative venture, but it’s essential to understand the various factors that affect profitability. From hardware and electricity costs to market conditions, several elements can influence your mining returns. This section aims to provide you with a detailed understanding of mining profitability and how to maximize it.
Factors Affecting Profitability
Electricity Costs
- Rate: The cost of electricity in your location can significantly impact your profitability.
- Consumption: The more power your mining rig consumes, the higher your electricity bill will be.
Hardware Efficiency
- Hash Rate: The higher the hash rate of your hardware, the more coins you can mine.
- Power Efficiency: Efficient hardware will consume less electricity for the same hash rate.
Market Prices
- Coin Value: The value of the cryptocurrency you’re mining will directly affect your earnings.
- Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices can be highly volatile, affecting your profitability in the short term.
Popular Mining Calculators
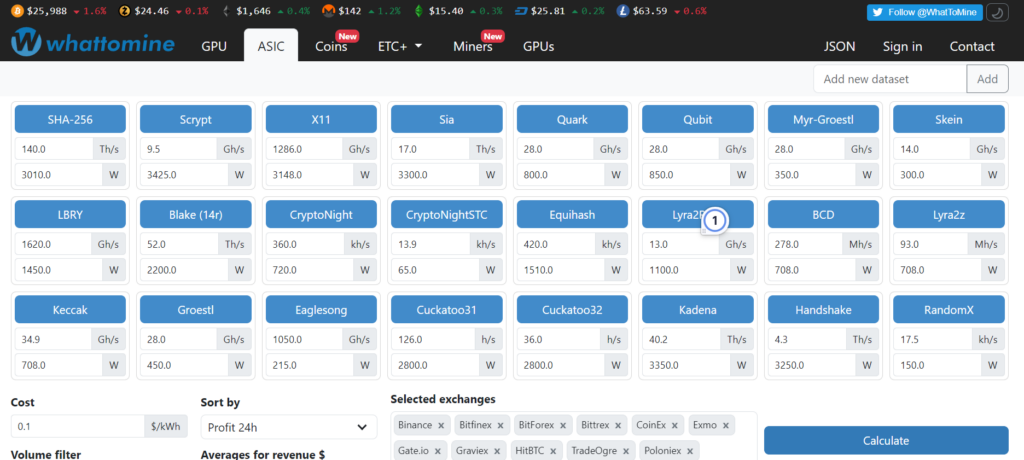
To get a more accurate estimate of your potential earnings, you can use mining calculators. Here are some popular options:
- WhatToMine: This tool provides a broad range of cryptocurrencies to choose from and considers various factors like hash rate, power consumption, and current market prices.
- WoolyPooly Calc: This calculator is user-friendly and offers a variety of coins to calculate profitability for. It also allows you to input your electricity costs for a more accurate estimate.
- Minerstat: While this tool is comprehensive and offers a wide range of cryptocurrencies, keep in mind that it tends to calculate 15-20% more profit than you should expect.
How to Maximize Profits
Choose Efficient Hardware
- Investing in hardware with a high hash rate and low power consumption can significantly increase your profitability.
Join a Reputable Mining Pool
- Mining pools can offer more consistent returns compared to solo mining.
Keep Track of Market Trends
- Being aware of market conditions can help you switch to more profitable coins when necessary.
Monitor and Optimize
- Regularly check your mining rig’s performance and make necessary adjustments to settings or hardware to maximize efficiency.
| Factor | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Electricity Costs | Rate, Consumption |
| Hardware Efficiency | Hash Rate, Power Efficiency |
| Market Prices | Coin Value, Volatility |
| Mining Calculators | WhatToMine, WoolyPooly Calc, Minerstat |
Risks and Challenges

Cryptocurrency mining can be a rewarding venture, but it’s not without its risks and challenges. Understanding these can help you make informed decisions and mitigate potential losses. Below are some of the key risks and challenges you should be aware of:
High Electricity Costs
- Impact: One of the most significant operational costs in mining is electricity. High electricity rates can quickly eat into your profits.
- Mitigation: Research electricity rates in your area and consider renewable energy sources or locations with lower electricity costs.
Hardware Wear and Tear
- Impact: Mining hardware is subjected to a lot of stress, leading to wear and tear. This can result in hardware failure and unexpected downtime.
- Mitigation: Regular maintenance, adequate cooling, and monitoring can prolong the lifespan of your hardware.
Market Volatility
- Impact: The value of cryptocurrencies can fluctuate wildly, affecting your profitability.
- Mitigation: Keep an eye on market trends and consider diversifying your mining activities across different cryptocurrencies.
Regulatory Risks
- Impact: Cryptocurrency regulations can vary by jurisdiction, and non-compliance can result in legal repercussions.
- Mitigation: Stay updated on local laws and regulations related to cryptocurrency mining and ensure you are compliant.
Security Risks
- Impact: Mining operations are susceptible to hacking, especially if proper security measures are not in place.
- Mitigation: Use secure and updated software, enable two-factor authentication, and take other cybersecurity measures.
Pool Risks
- Impact: Joining a mining pool can expose you to the risk of fraud or mismanagement by the pool operators.
- Mitigation: Research and choose reputable mining pools. Always read reviews and community feedback before joining.
Technical Complexity
- Impact: Setting up and maintaining a mining rig can be technically challenging, especially for beginners.
- Mitigation: Educate yourself through online resources, forums, and communities. Consider starting with simpler setups before moving on to more complex mining rigs.
Environmental Concerns
- Impact: Cryptocurrency mining, especially Proof of Work (PoW) mining, has been criticized for its environmental impact due to high energy consumption.
- Mitigation: Consider using energy-efficient hardware and renewable energy sources. Some miners are also exploring more eco-friendly consensus algorithms like Proof of Stake (PoS).
Conclusion
Embarking on the journey of cryptocurrency mining can be both exciting and challenging. As we’ve explored in this comprehensive guide on how to mine cryptocurrency, there are various aspects to consider—from choosing the right hardware and software to understanding the profitability and risks involved.
Mining is not just about setting up a rig and letting it run; it’s a venture that requires careful planning, ongoing maintenance, and a keen understanding of the ever-changing crypto landscape. Whether you opt for CPU, GPU, ASIC, or FPGA mining, each comes with its own set of advantages, challenges, and profitability metrics.
Understanding the electricity costs, market volatility, and technical complexities can help you navigate the hurdles that come with this endeavor. Utilizing tools like WhatToMine, WoolyPooly Calc, and Minerstat can provide valuable insights into your potential earnings and guide you in making informed decisions.
Moreover, being aware of the risks—from high operational costs and hardware wear and tear to regulatory and security risks—allows you to take preventive measures. This proactive approach can make the difference between a profitable mining operation and a failed one.
In summary, learning how to mine cryptocurrency is a multifaceted process that goes beyond merely solving mathematical problems. It’s about creating a well-oiled machine that operates efficiently, securely, and profitably. By taking the time to understand each aspect thoroughly, you’re setting yourself up for a more rewarding mining experience.
FAQs
Is mining still profitable?
Yes, but it depends on various factors like electricity costs and hardware efficiency.
How much can I earn from mining?
Earnings vary based on the type of mining and the current market conditions.
Is mining legal?
In most countries, yes, but always check local laws to be sure.


